Surface Window
Select View > Surface or click the Surface tab of the Aggregate Window to open the Surface Window. Use the Surface Window to apply surface attributes and textures to objects.
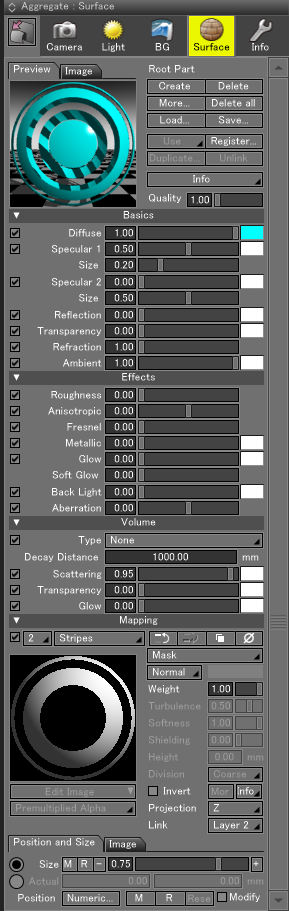
- Preview Tab
- A preview of the Basics, Effects, and Mapping settings is shown on the sphere.
- Image Tab
- After pasting a rendered image and then saving a Surface Settings file, this image will be used in any ShadeExplorer catalogs.
- Object Name
- Once surface settings for an object have been created, its name appears at the top of the Surface Window. If using a master surface, its name will also appear here.
- Create
- Applies the Surface Window settings to the selected object.
- Delete
- Deletes the surface attributes from the selected object.
- Advanced...
- Opens the Advanced Shading Dialog Box.
See also Advanced Shading Dialog Box
- Delete All
- Deletes all the surface attributes from the selected object and resets to default settings. If the selected object is a part, surface attributes for all nested objects are deleted as well.
- Load...
- Loads a surface settings file (.shdsfc, .xmlshdsfc).
- Save...
- Saves the current Surface Window settings as a surface settings file (.shdsfc, .xmlshdsfc).
- Use Pop-up Menu
- Click to select a master surface to use.
- Register...
- Opens a dialog for saving the current Surface Window settings as a master surface. If a master surface is currently selected, the Register button is not available.
- Duplicate...
- Copies the selected master surface.
- Unlink
- Unlinks the object's surface attributes from the master surface. Only available when the selected object is using a master surface.
- Info
- When a plugin with custom surface attributes is installed, click this button to display the custom attributes. When a plugin with custom surface attributes is installed, click this button to display the custom attributes.
In Shade3D Standard and Professional, the Toon Renderer Advanced Options are displayed. - Quality
- Specifies the quality as a ratio of the ray tracing quality in the Rendering Settings.
See also Surface Quality
Basic Settings
- Inherit Checkboxes
- Each surface attribute has an inherit checkbox to its left.
When selected, the attribute is not inherited from its parent, and can be modified. Changing the color for the attribute will automatically enable that setting.
Deselect the checkbox to inherit that attribute from the object's parent.
If a part is selected, holding Ctrl (Windows) or Option (Mac OS) when deselecting the inherit checkbox will deselect this checkbox for all objects inside the part. - Diffuse
- The intensity (brightness) of the diffuse reflection. Click the color box to open a color picker for selecting a different color. A color can also be dragged here from another color box.
- Specular 1
- The strength of the first specular value. Click the color box to open a color picker for selecting the Specular 1 color.
- Specular 1 Size
- The size of the first specular value.
- Specular 2
- The strength of the second specular value.
Note Specular 1 and Specular 2 are independent. Using both Specular 1 and Specular 2 allows more accurate simulation of coated surfaces. For example, for a coating with strong specular highlights, Specular 1 can be set with a large size and relatively weak intensity, and Specular 2 set with a small size and strong intensity. Click the color box to open a color picker for selecting the Specular 2 color.
- Specular 2 Size
- The size of the second specular value.
- Reflection
- The amount of reflection. Click the color box to open a color picker for selecting the reflected color.
- Transparency
- The transparency. Click the color box to open a color picker for selecting the transparency color. The transparency color is used for back pattern where the object is transparent, and the shadow.
- Refraction
- The refraction index.
- Ambient
- The amount of ambient light.
Note Unlike for distant lights, this is not a ratio of the light intensity.
Click the color box to open a color picker for selecting the color of the ambient light.
Effects Settings
- Roughness
- Valid for path tracing. The degree of surface roughness used for reflection and transparency.
- Anisotropic
- The anisotropic ratio. Setting anisotropic enables you to set the specular size of the object for the UV direction. This makes it possible to simulate the phenomenon in which specular highlights spread out in a definite direction in materials whose surfaces have a regular, fine unevenness, such as a metallic hairline finish or glossy cloth.
- Fresnel
- The fresnel reflection ratio. Fresnel reflection is a phenomenon in which the reflectance and transparency change according to the angle at which a material is viewed. Using fresnel reflection can improve the look of materials that reflect light, such as glass and plastic.
- Metallic
- The strength of metallic effect. Unrelated to actual lights in the scene, virtual specular is reflected on the object surface at random, simulating a metallic surface with specular highlights. The metallic result is similar to applying a spotted pattern and selecting Wrap from the Projection pop-up menu. Click the color box to open a color picker for selecting the color of the metallic effect.
- Glow
- The strength of glow (the intensity with which the object is irradiated). Click the color box to open a color picker for selecting the color of the glow.
- Soft Glow
- The sharpness of soft glow. The intensity and color of the Glow attribute are also used for Soft Glow. Soft glow simulates the glare of lights. This is actually a simulation of specular highlights on the object surface as seen from a distant light placed at the eye point. The Glow strength and color are substituted for the intensity and color of the virtual specular highlights, and the size of the virtual highlights is specified by the Soft Glow value. In order to simulate light glare, set the diffuse color to black and the specular to 0. If there is a background or other objects behind the object, transparency must also be set. If Glow is set to 0, Soft Glow will not be displayed.
- Back Light
- The strength of back lighting. Back lighting is the intensity at which light from the rear is reflected by the object. If transparency is set, the back light can be reflected onto other objects. Back light simulates the effect on an object surface of light coming from behind or inside the object, such as a silica-coated light bulb or a lampshade. Click the color box to open a color picker for selecting the back light color.
- Aberration
- The strength of color aberration. Aberration is only applicable to objects with transparency and refraction.
Volume Settings
The volume settings affect the interior properties of the object. Volume rendering is used for simulating translucent objects with volume. Subsurface scattering creates the effect of light scattering on an object surface, simulating soft textures such as skin.
The following volume settings apply to both Volume Rendering and Subsurface Scattering.
Note Volume Rendering is available in Shade3D Standard and Professional. Subsurface Scattering is only available in Professional.
Note The Volume settings can be controlled (restricted) from the Mapping settings.
- Type
- Select either Volume Rendering or Subsurface Scattering for the volume calculation method.
Note Volume rendering results will differ depending on whether the object is transparent or opaque. If the object is transparent, the volume rendering calculation result is multiplied by the transparency color. The refractive index and color of the object inside the volume are also taken into account. If the object is opaque, the volume rendering calculation result is used without additional factors. The refractive index and any object inside the volume are not affected.
- Decay Distance
- The density of the volume. The light intensity falls to 0 after light entering the object travels this distance. Smoke and similar effects can be simulated by controlling this with the mapping settings.
- Scattering
- The weight of the volume settings. Use the color box to specify the volume color.
- Transparency
- The weight of the color of the transparent part and the shadow cast by the volume.
Decay distance varies with the color. The formula for the decay distance of any color is decay distance divided by transparency color. Use the color box to set the color of the transparent part and the shadow cast by the volume. - Glow
- The weight of the volume glow color. Use to simulate a color, such as that of a flame, that is not affected by light intensity. Click the color box to open a color picker for selecting the volume glow color.
Mapping Settings
- Mapping Checkbox
- Select this checkbox to enable the mapping settings.
- Layer Pop-up Menu
- Specifies the layer index for the texture settings. Select New Layer to add a new layer. The name of the pattern applied to the selected layer is displayed to the right, in the Pattern pop-up menu. To layer multiple textures, select a new layer and then apply a different pattern. There is no limit to the number of textures that can be applied. By applying patterns to multiple layers, the textures can be blended. Blending is done for each surface attribute. The layer index indicates the layering order from bottom to top. The blend mode can be selected from the Blend pop-up menu.
- Pattern Pop-up Menu
- Specifies the pattern used for the selected layer.
Note Shade3D Professional includes an additional 10 solid textures to the ones described here.
See also Solid Texture - Move Layer Buttons
- Clicking
 will move the selected layer up one.
will move the selected layer up one.
Clicking will move the selected layer down one.
will move the selected layer down one. - Duplicate Layer
- Clicking
 will copy the selected layer. The new layer is added at the bottom.
will copy the selected layer. The new layer is added at the bottom. - Delete Layer
- Clicking
 will delete the selected layer.
will delete the selected layer. - Picture Box
- Shows a preview of the mapping settings. When a pattern other than Image is selected from the Pattern pop-up menu, the preview shows white blended with the below layer. When Image is selected, the preview shows the blend results using the selected Channel Blend Mode. The pop-up menu can also be opened by right-clicking (Win) or Control-clicking (Mac OS) the picture box.
- Edit Image Pop-up Menu
- Click to open a menu for working with the image used for the selected background layer.
Note In addition to the above menu items, in Shade3D Standard and Professional plugin options will be available. These options allow plugin features to be applied to the image.
- Channel Blend Mode Pop-up Menu
- Specifies the alpha channel blend method for the image's pixel colors. This option becomes available when Image is selected as the background pattern.
- Attribute Pop-up Menu
- Used to select the type of attribute applied to the selected layer.
- Blend Pop-up Menu
- Specifies the blend mode used for multiple layers.
- Weight
- Specifies the weight of the texture.
- Turbulence
- Available when Marble, Wood, Log, Wave, or Ocean is selected for the pattern. The degree of turbulence.
- Softness
- Available when Spotted is selected for the pattern. The sharpness of the spotted outline.
- Shielding
- The brightness of objects with environment mapping can be shielded to account for the reflections of surrounding objects.
See also Environment Map Object Shielding
- Height
- Available when Bump or Displacement is selected from the Attribute pop-up menu. Specifies the height of the bump map or displacement map.
- Division Pop-up Menu
- Available when Displacement is selected from the Attribute pop-up menu. Specifies the level of subdivision of the displacement map.
- Invert
- Inverts the colors of the mapping image. This is particularly effective at inverting the direction of a bump map or the holes of a mask layer.
- More... Button
- Opens a dialog for adjusting additional shading settings if a solid texture is selected from the Pattern pop-up menu.
See also Solid Texture
- Info Pop-up Menu
- When a plugin with custom mapping attributes is installed, click this button to display the custom attributes.
- Projection
- The available projection methods depend on the pattern selected.
- Link
- This menu is used to display mapping layers sharing mapping coordinates. Linking layers makes it possible to set and link multiple mapping layers. By selecting a mapping layer its mapping coordinates are integrated with the current mapping layer.
Note Available in Shade3D Standard and Professional.
Position and Size Tab
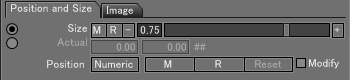
- Size
- Specifies the size of the pattern.
- Actual
- Enter an accurate texture size to set the pattern to this actual size.
Note Available in Shade3D Standard and Professional.
- Set...
- Opens the Set Mapping Origin dialog box for specifying the mapping origin.
See also Set Mapping Origin Dialog Box
- M Button
- Memorizes the current texture position.
- R Button
- Recalls the memorized texture position.
- Reset
- Resets the texture position to the point before it was modified using the Modify checkbox.
- Modify
- When selected, the mapping position and size can be modified.
Image Tab
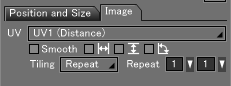
- UV
- This menu becomes available when Wrap is selected as the projection method. Specifies the image interpolation method. By default, UV1 (Distance) is selected.
- Smooth
- Applies antialiasing to the image before mapping it. This is effective when the image resolution is not quite high enough.
 Horizontal Flip
Horizontal Flip- This option becomes available when Image is selected as the background pattern. When selected, the image is flipped horizontally.
 Vertical Flip
Vertical Flip- This option becomes available when Image is selected as the background pattern. When selected, the image is flipped vertically.
 Switch Axes
Switch Axes- This option becomes available when Image is selected as the background pattern. When selected, the image's horizontal and vertical axes are switched.
- Tiling
- This checkbox becomes available when using projections other than Wrap. Select from None, Repeat, Mirror, and Edge.
See also Image Tiling Patterns
- Repeat
- Enter a number (or select a number from the pop-up menu) to specify the number of horizontal and vertical repetitions for the mapped image. The pop-up menus can be used to select a number between 1 and 10. Use the text box to enter numbers greater than 10. The left text box and pop-up menu specify the number of horizontal repetitions; the text box and pop-up menu on the right specify the number of vertical repetitions.