scene
Basic class used to get or set information about the scene.
| xshade |
| ↑ |
| scene |
List of Methods
| active_shape | Returns the selected object |
| adjust_transformation | Resets matrices except for translation of the selected object |
| append | Appends the memorized line object to the selected object |
| append_metacamera | Appends a meta-camera |
| append_point | Appends a control point to the line object being created |
| append_polygon_mesh_edge | Appends an edge to a polygon mesh either being created or selected |
| append_polygon_mesh_edges | Generates the necessary edges for a polygon mesh without edges |
| append_polygon_mesh_face | Appends an face to a polygon mesh either being created or selected |
| append_polygon_mesh_vertex | Appends a vertex to a polygon mesh either being created or selected |
| append_truetype_point | Appends a point to a TrueType (two-dimensional Bezier curve) object being created |
| apply | Applies the memorized line object to the selected object |
| begin_ball_joint | Begins creation of a ball joint |
| begin_bone_joint | Begins creation of a bone joint |
| begin_creating | Begins creation of an object |
| begin_creating_at | Begins creation of an object at the specified insertion point |
| begin_custom_joint | Begins creation of a custom joint |
| begin_light_effector | Begins creation of a light joint |
| begin_line | Begins creation of a line object |
| begin_morph_effector | Begins creation of a morph joint |
| begin_part | Begins the creation of a part |
| begin_path_joint | Begins creation of a path joint |
| begin_path_replicator | Begins creation of a path replicator |
| begin_polygon_mesh | Begins creation of a polygon mesh |
| begin_rotator_joint | Begins creation of a rotator joint |
| begin_scale_joint | Begins creation of a scale joint |
| begin_slider_joint | Begins creation of a slider joint |
| begin_sound_object | Begins creation of a sound object |
| begin_surface_part | Begins the creation of curved surface part |
| begin_surface_replicator | Begins creation of a surface replicator |
| begin_switch_effector | Begins creation of a switch |
| begin_truetype | Begins creation of a TrueType (two-dimensional Bezier curve) object |
| begin_uniscale_joint | Begins creation of a uniscale joint |
| bevel_edge | Apply Bevel Edge |
| browser_active | Displays the currently selected object in the Browser |
| cancel_line_object | Cancels the creation of a line object |
| cancel_transformation | Offsets the transformation |
| clear | Deletes the selected object |
| clear_memory | Clears data memorized with the Memory tool |
| clear_template | Deletes the template image |
| clear_transformation | Resets the transformation |
| close | Closes the scene |
| close_scene | Closes the scene |
| convert_to_curved_surface | Converts the selected object to a curved surface |
| convert_to_line_object | Converts the selected object to a line object |
| convert_to_polygon_mesh | Converts the selected object to a polygon mesh |
| copy | Copies the selected object to the clipboard |
| copy_object | Duplicates the object and applies rotation, scaling, or translation |
| create_ball_joint | Creates a ball joint |
| create_bone_joint | Creates a bone joint |
| create_camera | Creates a camera object |
| create_custom_joint | Creates a custom joint |
| create_disk | Creates a disk |
| create_light_effector | Creates a light joint |
| create_line | Creates a line object |
| create_local_axis | Creates a (temporary) coordinate system from the selected object |
| create_master_image | Creates a master image |
| create_master_surface | Creates a master surface |
| create_morph_effector | Creates a morph joint |
| create_offset_lines | Creates an offset lines |
| create_part | Creates a part |
| create_path_joint | Creates a path joint | create_path_replicator | Creates a path replicator |
| create_point_light | Creates a point light |
| create_primitive_box | Creates a cube |
| create_primitive_capsule | Creates a capsule |
| create_primitive_cone | Creates a cone |
| create_primitive_cylinder | Creates a cylinder |
| create_primitive_plane | Creates a rectangle |
| create_primitive_pyramid | Creates a triangular pyramid |
| create_primitive_sphere | Creates a sphere |
| create_primitive_text | Creates a 3D text |
| create_primitive_torus | Creates a torus |
| create_rotator_joint | Creates a rotator joint |
| create_scale_joint | Creates a scale joint |
| create_slider_joint | Creates a slider joint |
| create_sound_object | Creates a sound object |
| create_sphere | Creates a sphere |
| create_spotlight | Creates a spotlight |
| create_surface_part | Creates a curved surface part |
| create_surface_replicator | Creates a surface replicator |
| create_switch_effector | Creates a switch |
| create_uniscale_joint | Creates a uniscale joint |
| cut | Cuts the selected object to the clipboard |
| degenerate | Degenerates to a point |
| deselect_all_key_points | Deselects all motion points |
| draw_figure_window | Draws the Figure Window |
| end_ball_joint | Ends creation of a ball joint |
| end_bone_joint | Ends creation of a bone joint |
| end_creating | Ends creation of an object |
| end_custom_joint | Ends creation of a custom joint |
| end_light_effector | Ends creation of a light joint |
| end_line | Ends creation of an line object |
| end_morph_effector | Ends creation of a morph joint |
| end_part | Ends creation of a part |
| end_path_joint | Ends creation of a path joint |
| end_path_replicator | Ends creation of a path replicator |
| end_polygon_mesh | Ends creation of a polygon mesh |
| end_rotator_joint | Ends creation of a rotator joint |
| end_scale_joint | Ends creation of a scale joint |
| end_slider_joint | Ends creation of a slider joint |
| end_sound_object | Ends creation of a sound object |
| end_surface_part | Ends creation of a curved surface part |
| end_surface_replicator | Ends creation of a surface replicator |
| end_switch_effector | Ends creation of a switch |
| end_truetype | Ends creation of a TrueType (two-dimensional Bezier curve) object |
| end_uniscale_joint | Ends creation of a uniscale joint |
| enter_create_line_mode | Enters Create Line Mode |
| enter_modify_mode | Enters Modify Mode |
| exit_create_line_mode | Exits Create Line Mode |
| exit_modify_mode | Exits Modify Mode |
| export_scene | Exports the scene data |
| export_with_uuid | Exports the file with uuid |
| fit_to_window | Fits object to the Figure Window |
| flip_hide_faces | In Modify Mode, flips between hidden and nonhidden faces |
| force_update | Forces a screen redraw |
| get_grid_shown | Returns the grid on/off value of the specified viewport |
| get_ik | Gets the IK handling class |
| get_shape_by_name | Returns an object with the specified name |
| get_shape_by_ordinal | Returns an object specified by ordinal number |
| get_shape_by_position | Returns an object by position in the Browser |
| get_shape_by_uuid | Returns an object specified by uuid |
| get_shapes_by_name | Returns a tuple of objects with the specified name |
| get_view_rectangle | Returns the rectangular display area of the view specified by argument |
| hide_active | Hides the selected object |
| hide_inactive | Hides unselected objects |
| hide_select_faces | In Modify Mode, hides the selected faces of the selected object |
| hide_unselect_faces | In Modify Mode, hides the unselected faces of the selected object |
| iron | Applies Iron |
| link | Links the selected part to the memorized object |
| link_object | Creates a link object referencing the selected object |
| load_3DS | Imports a 3DS file |
| load_BVH | Imports a BVH file |
| load_DXF | Imports a DXF file |
| load_OBJ | Imports a wavefront OBJ file |
| load_pose | Imports a Shade Pose file |
| load_shape | Imports Shade object data |
| load_template_image_to_front_view | Loads a template in the bottom left viewport |
| load_template_image_to_pers_view | Loads a template in the top right viewport |
| load_template_image_to_side_view | Loads a template in the bottom right viewport |
| load_template_image_to_top_view | Loads a template in the top left viewport |
| load_text | Imports an XML text file |
| magnify | Magnifies the Figure Window |
| memorized_shape | Returns the memorized object |
| memory | Memorizes the selected line object |
| move_object | Applies rotation, scaling, or translation to an object |
| paste | Pastes an object into the scene from the clipboard |
| place_brother | Moves the selected object down |
| place_child | Moves the selected object inside the below part |
| place_parent | Moves the selected object to the top of the above hierarchy level |
| place_sister | Moves the selected object forward |
| print_ | Prints the rendered image |
| read | Loads a scene from file |
| repeat | Applies Repeat |
| reset_all_transformation | Resets the matrices of all parts within the selected part to unit matrices |
| reset_transformation | Resets the matrix of the selected part to a unit matrix |
| reverse | Applies Reverse |
| revert_to_saved | Reverts the open Shade file to the saved state |
| round_edge | Applies Round Edge |
| save | Saves over the current scene |
| save_3DS | Exports as a 3DS file |
| save_Animation_Master | Exports as an Animation:Master segment file |
| save_as | Displays a file dialog and saves the scene to file. |
| save_DXF | Exports as a DXF file |
| save_EPX | Exports as an EPix file |
| save_FBX | Exports as an FBX file |
| save_image | Saves the rendered image to file |
| save_images | Saves the rendered image to file in multi-layer format |
| save_local_axis | Saves the coordinate system (used temporarily) |
| save_OBJ | Exports as a wavefront OBJ file |
| save_pose | Exports a pose file |
| save_RIB | Exports as a RIB file |
| save_shape | Exports as a Shade Shape file |
| save_text | Exports as an XML text file |
| save_VRML | Exports as a VRML file |
| save_VRML_2 | Displays a file dialog and exports as a VRML file |
| scroll | Scrolls the Figure Window |
| select_all | Selects the Root Part |
| select_brother | Selects the object after the selected object |
| select_child | Selects the objects in the part below the selected object |
| select_parent | Selects the part above the selected object in the hierarchy |
| select_sister | Selects the object before the selected object |
| sequence_world_to_device_matrix | Returns a matrix that converts the world coordinate system of the specified sequence to device coordinates |
| sequence_world_to_perspective_matrix | Returns a matrix that converts the world coordinate system of the specified sequence to perspective coordinates |
| sequence_world_to_view_matrix | Returns a matrix that converts the world coordinate system of the specified sequence to view coordinates |
| set_grid_shown | Sets the grid on/off value of the specified viewport |
| show_active | Displays the selected object |
| show_all | Displays all objects |
| show_all_faces | In Modify Mode, displays all the faces of the selected object |
| shrink | Shrinks the Figure Window |
| smooth | Applies Smooth |
| solid_clear | Returns the original state of an extruded or revolved solid |
| solid_extrude | Creates an extruded solid |
| solid_revolve | Creates a revolved solid |
| sweep | Applies Sweep |
| switch | Applies Switch |
| unsmooth | Applies Unsmooth. |
| update_figure_window | Redraws the Figure Window. |
| use_global | Uses global coordinates for the Figure Window display. |
| use_local | Uses the local coordinates of the selected object for the Figure Window display. |
| use_local_axis | Uses the specified coordinate system |
| write | Saves a Shade scene file |
| write_compatible | Saves a Shade scene file after adding compatibility information |
| write_noncompatible | Saves a Shade scene file without adding compatibility information |
| write_R4compatible | Saves a Shade scene file after adding R4 compatibility information |
| write_xml | Saves a Shade scene file as XML |
List of Properties
| active_shapes | The list of currently selected objects |
| animation_settings | Animation of the scene |
| background | Background of the scene |
| camera | The currently selected camera in the scene |
| can_create | Whether or not there is a functional restriction on creating new objects |
| can_export_foreign | Whether or not there is a functional restriction on exporting to formats unrelated to Shade |
| can_export_native | Whether or not there is a functional restriction on exporting to Shade-related formats |
| can_save | Whether or not there is a functional restriction on saving the scene |
| can_save_rendered_image | Whether or not there is a functional restriction on saving the rendered image to file |
| center | The coordinates of the center of each of the viewports, other than the perspective view |
| color_mode | Color mode of the Figure Window display |
| correction | Color correction of the scene |
| current_camera | The index value of the currently selected camera |
| current_cursor_position | Current coordinates value of the 3D cursor in the Figure Window |
| cursor_plane | The cursor plane in the perspective view |
| cursor_position | Coordinates value of the 3D cursor in the Figure Window (the clicked position) |
| default_bevel_radius | Default value of Round Edge and Bevel Edge |
| default_disk_radius | Default radius of a disk |
| default_light_radius | Default light intensity |
| default_radius | Default radius of Round Edge and Bevel Edge for line objects |
| default_sphere_radius | Default radius of a sphere |
| dirty | Whether or not the scene is dirty |
| display | Figure Window of the scene |
| distant_light | Distant Light of the scene |
| figure_view_mode | Figure Window view mode |
| figure_window | Figure Window of the scene |
| file_path | File path of the saved scene |
| fog | Distant Light Fog of the scene |
| fps | Scene fps |
| grid | Grid display on/off |
| insertion_shape | Shape class of the object at the inserted position when creating an object with begin_creating(). |
| is_create_line_mode | Whether or not in Create Line Mode |
| is_locked | Whether or not the file is locked |
| is_modify_mode | Whether or not in Modify Mode |
| is_motion_playing | Whether or not the Motion Window is playing |
| keyframes | Keyframes of the scene |
| large_cursor | Large Cursor display on/off |
| large_point | Large Point display on/off |
| lathe_rotation | Lathe rotation |
| light_scale | Light scale |
| local | Reference part of the local coordinates |
| local_matrix | Local coordinates mode transformation matrix |
| manip_type | The manipulator type |
| mapping_modify_mode | Whether or not in Mapping Modify Mode |
| native_to_user_unit | Coefficient which converts native units (mm) to user-defined units |
| number_of_appended_points | The number of control points of the line object being created |
| number_of_cameras | The number of cameras |
| number_of_memorized_shapes | The number of memorized objects |
| number_of_metacameras | The number of meta-cameras |
| pers_grid | Perspective Grid display on/off |
| pivot_position | The pivot coordinates |
| pixel_size | The state of magnification of the Figure Window |
| radiosity | Radiosity of the scene |
| rendering | Rendering of the scene |
| selection_method | The Toolbox Selection Mode |
| selection_mode | The Mesh Selection Mode |
| sequence_mode | Whether the scene is in Sequence Mode or not |
| sequence_value | The sequence value of the Motion Window |
| shape | The root object |
| show_normals | Whether to show normals or not |
| snap | Snap on/off |
| step_frames | The number of step frames of the animation (float) |
| template | Template display on/off |
| unit | The unit value |
| user_to_native_unit | Coefficient which converts user-defined units to native units (mm) |
| user_to_world_matrix | Matrix that converts the user coordinate system to world coordinates |
| window_frame | The Figure Window frame |
| work_plane | Work plane on/off |
| world_to_device_matrix | Matrix that converts the world coordinate system to device coordinates |
| world_to_perspective_matrix | Matrix that converts the world coordinate system to the perspective coordinate system of the active camera |
| world_to_user_matrix | Matrix that converts the world coordinate system to user coordinates |
| world_to_view_matrix | Matrix that converts the world coordinate system to the view coordinate system of the active camera |
Method Details
active_shape
Returns the selected object.
Return value :
shape object
Arguments :
int : index of the selected object : Optional if there is only one object or when getting the root object.
#Output the name of the selected object
print xshade.scene().active_shape().name
adjust_transformation
Resets matrices except for translation of the selected object.
Transformation elements attached to the object are preserved as-is.
xshade.scene().adjust_transformation()
append
Appends the memorized line object to the selected object.
xshade.scene().append()
append_metacamera
Appends a meta-camera.
xshade.scene().append_metacamera()
append_point
Appends a control point to the line object being created.
Arguments :
vec3 : point : position of the anchor point
Arguments :
vec3 : position of the in-handle
Arguments :
vec3 : position of the out-handle
Arguments :
vec3 : position of the intersecting in-handle
Arguments :
vec3 : the intersecting out-handle
The local coordinate system at the hierarchy where the object is created becomes the reference.
See also :
begin_creating()
begin_line()
end_line()
end_creating()
#Append a control point at two locations of the line object being created
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_line(None, True)
xshade.scene().append_point([0.0, 0.0, 0.0], None, None, None, None)
xshade.scene().append_point([1000.0, 1000.0, 0.0], None, None, None, None)
xshade.scene().end_line()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
append_polygon_mesh_edge
Appends an edge to a polygon mesh either being created or selected.
Arguments :
int : index value of one vertex of the edge
Arguments :
int : index value of the edge's other vertex
See also :
begin_creating()
begin_polygon_mesh()
end_polygon_mesh()
end_creating()
xshade.scene().append_polygon_mesh_edge(0,1)
append_polygon_mesh_edges
Generates the necessary edges for a polygon mesh without edges.
xshade.scene().append_polygon_mesh_edges()
append_polygon_mesh_face
Appends a face to a polygon mesh either being created or selected.
Arguments :
int : list/tuple of the vertex indices
See also :
begin_creating()
begin_polygon_mesh()
end_polygon_mesh()
end_creating()
xshade.scene().append_polygon_mesh_face([0,1,2,3])
append_polygon_mesh_vertex
Appends a vertex to a polygon mesh either being created or selected.
Arguments :
vec3
The local coordinate system of the hierarchy being created or currently selected becomes the reference.
See also :
begin_creating()
begin_polygon_mesh()
end_polygon_mesh()
end_creating()
xshade.scene().append_polygon_mesh_vertex((100,200,0))
append_truetype_point
Appends a point to a TrueType (two-dimensional Bezier curve) object being created.
Arguments :
bool : ONポイントかどうか
Arguments :
float : the X coordinate value
Arguments :
float : the Y coordinate value
Arguments :
float : the Z coordinate value : optional (0 if omitted)
Call between begin_truetype() and end_truetype().
The local coordinate system at the hierarchy where the object is created becomes the reference.
#Create a TrueType object composed of 3 points
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_truetype(None, False)
xshade.scene().append_truetype_point(True,0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
xshade.scene().append_truetype_point(False,100.0, 100.0, 0.0)
xshade.scene().append_truetype_point(True,200.0, 0.0, 0.0)
xshade.scene().end_truetype()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
apply
Applies the memorized line object to the selected object.
xshade.scene().apply()
begin_ball_joint
Begins creation of a ball joint.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
vec3 : center position
Arguments :
float : radius
Arguments :
string : optional If omitted, the default name is used
It is possible to include objects created until calling end_ball_joint() inside a part.
The local coordinate system at the hierarchy where the object is created becomes the reference.
#Create a ball joint at the origin with radius 100
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_ball_joint((0.0,0.0,0.0),100)
xshade.scene().end_ball_joint()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
begin_bone_joint
Begins creation of a bone joint.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
vec3 : center position
Arguments :
float : radius
Arguments :
bool : Auto Align to axis
Arguments :
vec3 : The axis direction when doing Auto Align Axis : optional : If omitted, the default settings are applied
Arguments :
string : optional If omitted, the default name is used
It is possible to include objects created until calling end_bone_joint() inside a part.
The local coordinate system at the hierarchy where the object is created becomes the reference.
#Create a bone with radius 100 and length 800 in the X direction starting at the origin, and apply Auto Align in the Y axis direction
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
b1=xshade.scene().begin_bone_joint([0.0,0.0,0.0],100,True,[0.0,1.0,0.0])
b2=xshade.scene().begin_bone_joint([800.0,0.0,0.0],100,True,[0.0,1.0,0.0])
xshade.scene().end_bone_joint()
xshade.scene().end_bone_joint()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
begin_creating
Begins creation of an object.
When calling a function for creating an object, always use with end_creating().
If specifying the position of the created object, use begin_creating_at().
If omitted, Shade will process begin_creating() and end_creating() internally, slowing down the processing speed.
#If begin/end is used each time a part is created, the parts will be nested xshade.scene().begin_creating() xshade.scene().begin_part() xshade.scene().end_part() xshade.scene().end_creating() xshade.scene().begin_creating() xshade.scene().begin_part() xshade.scene().end_part() #If begin/end is used only once, the parts will be parallel xshade.scene().begin_creating() xshade.scene().begin_part() xshade.scene().end_part() xshade.scene().begin_part() xshade.scene().end_part() xshade.scene().end_creating()
begin_creating_at
Begins creation of an object at the specified insertion point.
Arguments :
insertion_point : shape object : the shape class of the object at the insertion point
When calling a function for creating an object, always use with end_creating().
#Create a part positioned above (sister to) the selected object
shape = xshade.scene().active_shape().sis
xshade.scene().begin_creating_at(shape)
xshade.scene().begin_part()
xshade.scene().end_part()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
begin_custom_joint
Begins creation of a custom joint.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
It is possible to include objects created until calling end_custom_joint() inside a part.
#Create a custom joint
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_custom_joint()
xshade.scene().end_custom_joint()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
begin_light_effector
Begins creation of a light joint.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
It is possible to include objects created until calling end_light_effector() inside a part.
#Create a light joint
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_light_effector()
xshade.scene().end_light_effector()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
begin_line
Begins creation of a line object.
Return value :
line object
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
Arguments :
bool : True : closed line object : False : open line object
Use together with end_line().
Create control points using append_point().
The local coordinate system at the hierarchy where the object is created becomes the reference.
#Create an open line object composed of 2 points
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_line(None, False)
xshade.scene().append_point([0.0, 0.0, 0.0], None, None, None, None)
xshade.scene().append_point([0.0, 500.0, 0.0], None, None, None, None)
xshade.scene().end_line()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
begin_morph_effector
Begins creation of a morph joint.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
#Create a morph joint
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_morph_effector()
xshade.scene().end_morph_effector()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
begin_part
Begins the creation of a part.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
It is possible to include objects created until calling end_part() inside a part.
#Create a part
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_part()
xshade.scene().end_part()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
begin_path_joint
Begins creation of a path joint.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
#Create a path joint
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_path_joint()
xshade.scene().end_path_joint()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
begin_path_replicator
Begins creation of a path replicator.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
#Create a path replicator
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_path_replicator()
xshade.scene().end_path_replicator()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
begin_polygon_mesh
Begins creation of a polygon mesh.
Return value :
polygon_mesh object
Arguments :
string : optional : If "None", the default name is used
Use together with end_polygon_mesh().
Create vertices with append_polygon_mesh_vertex().
Create edges with append_polygon_mesh_edg().
The necessary faces are automatically created.
The local coordinate system at the hierarchy where the object is created becomes the reference.
#Create a polygon mesh composed of 3 vertices and 3 edges
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_polygon_mesh(None)
xshade.scene().append_polygon_mesh_vertex([0.0,0.0,0.0])
xshade.scene().append_polygon_mesh_vertex([100.0,0.0,0.0])
xshade.scene().append_polygon_mesh_vertex([50.0,100.0,0.0])
xshade.scene().append_polygon_mesh_edge(0,1)
xshade.scene().append_polygon_mesh_edge(1,2)
xshade.scene().append_polygon_mesh_edge(2,0)
xshade.scene().end_polygon_mesh()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
begin_rotator_joint
Begins creation of a rotator joint.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
vec3 : position of one end point of the axis
Arguments :
vec3 : position of the other end point of the axis
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
It is possible to include objects created until calling end_rotator_joint() inside a part.
The local coordinate system at the hierarchy where the object is created becomes the reference.
#Create a rotator joint with length 100 along the Y axis starting at the origin
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_rotator_joint((0.0,0.0,0.0),(0.0,100.0,0.0))
xshade.scene().end_rotator_joint()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
begin_scale_joint
Begins creation of a scale joint.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
vec3 : the center point
Arguments :
vec3 : the target point
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
It is possible to include objects created until calling end_scale_joint() inside a part.
The local coordinate system at the hierarchy where the object is created becomes the reference.
#Create a scale joint of length 100 along the Y axis starting at the origin
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_scale_joint((0.0,0.0,0.0),(0.0,100.0,0.0))
xshade.scene().end_scale_joint()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
begin_slider_joint
Begins creation of a slider joint.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
vec3 : the starting point
Arguments :
vec3 : the ending point
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
It is possible to include objects created until calling end_slider_joint() inside a part.
The local coordinate system at the hierarchy where the object is created becomes the reference.
#Create a slider joint of length 100 along the Y axis starting from the origin
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_slider_joint((0.0,0.0,0.0),(0.0,100.0,0.0))
xshade.scene().end_slider_joint()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
begin_sound_object
Begins creation of a sound object.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
file_path
Arguments :
vec3 : the center point
Arguments :
float : radius
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
Use together with end_sound_object().
The local coordinate system at the hierarchy where the object is created becomes the reference.
#Create a sound object at the origin, with radius 100, from an aiff sound file
dialog = xshade.create_dialog_with_uuid()
file_path = dialog.ask_path(True, '*.aiff|aiff')
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_sound_object(file_path,(0.0,0.0,0.0),100)
xshade.scene().end_sound_object()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
begin_surface_part
Begins the creation of curved surface part.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
It is possible to include line objects created until calling end_surface_part() inside a part.
#Create a curved surface part
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_surface_part()
xshade.scene().end_surface_part()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
begin_surface_replicator
Begins creation of a surface replicator.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
It is possible to include objects created until calling end_surface_replicator() inside a part.
#Create a surface replicator
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_surface_replicator()
xshade.scene().end_surface_replicator()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
begin_switch_effector
Begins creation of a switch.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
It is possible to include objects created until calling end_switch_effector() inside a part.
#Create a switch
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_switch_effector()
xshade.scene().end_switch_effector()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
begin_truetype
Begins creation of a TrueType (two-dimensional Bezier curve) object.
Return value :
line object
Arguments :
string : If "None", the default name is used
Arguments :
bool : is hole object or not
Use together with end_truetype()
Create points with append_truetype_point()
#Create a TrueType object composed of 3 points
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_truetype(None, False)
xshade.scene().append_truetype_point(True,0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
xshade.scene().append_truetype_point(False,100.0, 100.0, 0.0)
xshade.scene().append_truetype_point(True,200.0, 0.0, 0.0)
xshade.scene().end_truetype()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
begin_uniscale_joint
Begins creation of a uniscale joint.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
vec3 : the center point
Arguments :
float : radius
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
It is possible to include objects created until calling end_uniscale_joint() inside a part.
The local coordinate system at the hierarchy where the object is created becomes the reference.
#Create a uniscale joint with radius 100 at the origin
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_uniscale_joint((0.0,0.0,0.0),100)
xshade.scene().end_uniscale_joint()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
bevel_edge
Apply Bevel Edge.
Arguments :
float : radius
#Apply Bevel Edge with radius of 20.5
xshade.scene().bevel_edge(20.5)
browser_active
Displays the currently selected object in the Browser.
xshade.scene().browser_active()
cancel_line_object
Cancels the creation of a line object.
#Cancel creation of a line object when flag is True
boolFlag = True
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_line(None, True)
xshade.scene().append_point([0.0, 0.0, 0.0], None, None, None, None)
xshade.scene().append_point([0.0, 500.0, 0.0], None, None, None, None)
if boolFlag:
xshade.scene().cancel_line_object()
else:
xshade.scene().end_line()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
cancel_transformation
Offsets the transformation.
Offsets the transformation on the above part.
xshade.scene().cancel_transformation()
clear
Deletes the selected object.
xshade.scene().clear()
clear_memory
Clears data memorized with the Memory tool.
xshade.scene().clear_memory()
clear_template
Deletes the template image.
xshade.scene().clear_template()
clear_transformation
Resets the transformation.
The transformation on the object is also cleared
xshade.scene().clear_transformation()
close
Closes the scene.
xshade.scene().close()
close_scene
Closes the scene.
Arguments :
bool : Confirmation of scene changes : False : Close the scene without confirmation : (False) must be defined
xshade.scene().close_scene(False)
convert_to_curved_surface
Converts the selected object to a curved surface.
xshade.scene().convert_to_curved_surface()
convert_to_line_object
Converts the selected object to a line object.
xshade.scene().convert_to_line_object()
convert_to_polygon_mesh
Converts the selected object to a polygon mesh.
Arguments :
int : number of subdivisions in the direction of intersection
Arguments :
int : number of subdivisions in the direction of the selection
#Intersection 4, Selection 2 to convert into polygon mesh
xshade.scene().convert_to_polygon_mesh(4,2)
copy
Copies the selected object to the clipboard.
xshade.scene().copy()
copy_object
Duplicates the object and applies rotation, scaling, or translation.
Arguments :
vec3 : the center point
Arguments :
float3 : scale
Arguments :
float3 : rotation
Arguments :
float3 : translation
See also :
move_object
#Copy the object, scale it by 1.5 in all directions, and move it 250 along the X axis
xshade.scene().copy_object([0.0, 0.0, 0.0], [1.5, 1.5, 1.5], None, [250.0, 0.0, 0.0])
create_ball_joint
Creates a ball joint.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
vec3 : center position
Arguments :
float : radius
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
The local coordinate system at the hierarchy where the object is created becomes the reference.
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
#Create a ball joint with radius 100 at the origin
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().create_ball_joint([0.0, 0.0, 0.0],100)
xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_bone_joint
Creates a bone joint.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
vec3 : center position
Arguments :
float : radius
Arguments :
bool : Auto Align to axis
Arguments :
vec3 : The axis direction when doing Auto Align Axis : optional : If omitted, the default settings are applied
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
The local coordinate system at the hierarchy where the object is created becomes the reference.
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
#Create a bone joint with radius 100 at the origin and apply Auto Align in the direction of the Y axis
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
b1=xshade.scene().create_bone_joint([0.0, 0.0, 0.0],100,true,[0.0, 1.0, 0.0])
xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_camera
Creates a camera object.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
vec3 : the eye point
Arguments :
vec3 : the target point
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
The local coordinate system at the hierarchy where the object is created becomes the reference.
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
#Create a camera with eye point at origin and target point at [0.0, 100.0, 100.0]
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().create_camera([0.0, 0.0, 0.0],[0.0, 100.0, 100.0])
xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_custom_joint
Creates a custom joint.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
xshade.scene().begin_creating() xshade.scene().create_custom_joint() xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_disk
Creates a disk.
Return value :
disk object
Arguments :
string : optional : If "None", the default name is used
Arguments :
vec3 : position
Arguments :
float : radius
Arguments :
int :
| 0 | X axis |
| 1 | Y axis |
| 2 | Z axis |
| 3 | eye-target axis |
The local coordinate system at the hierarchy where the object is created becomes the reference.
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
#Create a disk at the origin with radius 100 along the X axis
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().create_disk(None,[0.0, 0.0, 0.0], 100,0)
xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_light_effector
Creates a light joint.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
xshade.scene().begin_creating() xshade.scene().create_light_effector() xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_line
Creates a line object.
Return value :
line object
Arguments :
string : optional : If "None", the default name is used
Arguments :
vec3 tuple/list : array of control point coordinates
Arguments :
bool : True: closed line object, False: open line object
The local coordinate system at the hierarchy where the object is created becomes the reference.
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
#Create a closed line object composed of 3 control points
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().create_line(None,[[0,0,0],[100,0,0],[100,100,0]],True)
xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_local_axis
Creates a (temporary) coordinate system from the selected object.
Return value :
part
See also :
save_local_axis
xshade.scene().create_local_axis()
create_master_image
Creates a master image.
Return value :
image object
Arguments :
string : optional : If "None", the default name is used
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
If omitted, the Browser must be updated or the results will not take effect.
#Create a master image to which a copy of the rendered image is assigned
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
img_obj = xshade.scene().create_master_image('sample')
img_obj.image = xshade.scene().rendering.image.duplicate()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_master_surface
Creates a master surface.
Return value :
master_surface object
Arguments :
string : optional : If "None", the default name is used
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
xshade.scene().begin_creating() xshade.scene().create_master_surface(None) xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_morph_effector
Creates a morph joint.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
xshade.scene().begin_creating() xshade.scene().create_morph_effector() xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_offset_lines
Creates an offset lines
Return value :
None
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
Arguments :
float : Distance
Arguments :
vec3 : Plane Coordinate : [0,1,0] : XZ-Plane、[0,0,1] : XY-Plane、[1,0,0] : ZY-Planebr />
Arguments :
int : Offset Direction : -1 :One-sided (Anti-clockwise), 0 : Both sides, 1 : One-sided (Clockwise)
Arguments :
int : Edge Style : 0 : Miter, 1 : Bevel, 2 : Round 1, 3 : Round 2
Arguments :
int : Roundness : -1 ~ 3.0
Arguments :
int : Repetition Count
Arguments :
int : Slope Distance : -1.0 ~ 1.0
Arguments :
int : Distance to : 0 : Nearest Line, 1 : Most Distant Line
Arguments :
float : Vertical Distance in Repetition
Arguments :
int : Height Distribution : -1.0 ~ 1.0
Arguments :
int : Height to : 0 : Nearest Line, 1 : Most Distant Line
Arguments :
bool : Allow to add control points : True :Yes, False :No
Arguments :
bool : Delete Original Shapes : True :Yes, False :No
begin_creating()、end_creating() are optional.
#YZ Plane Coordinate:200, Offset Direction:Both sides, Edge Style:Round 1, Roundness:1.5, Repetition Count:2, Slope Distance:0.3, Distance to:Nearest Line, Vertical Distance in Repetition:40, Height Distribution:50, Height to:Nearest Line, Allow to add control points:True, No Delete Original Shapes:False
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().create_offset_lines(200.0, [0, 1, 0], 0, 2, 1.2, 2, 0.1, 0, 10, 0.3, 0, True, False)
xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_part
Creates a part.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
xshade.scene().begin_creating() xshade.scene().create_part() xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_path_joint
Creates a path joint.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
xshade.scene().begin_creating() xshade.scene().create_path_joint() xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_path_replicator
Creates a path replicator.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
xshade.scene().begin_creating() xshade.scene().create_path_replicator() xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_point_light
Creates a point light.
Return value :
light object
Arguments :
string : optional : If "None", the default name is used
Arguments :
vec3 : position
Arguments :
float : radius
The local coordinate system at the hierarchy where the object is created becomes the reference.
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
#Create a point light at the origin with radius 100
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().create_point_light(None,[0.0, 0.0, 0.0],100)
xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_primitive_box
Creates a cube.
Return value :
object
Arguments :
string : If "None", the default name is used
Arguments :
int : object type : 0 : generic, 1 : curved surface, 2 : unused, 3 : polygon mesh
Arguments :
bool : UV assigned : Not valid except for polygon meshes
Arguments :
int : number of X direction subdivisions : Not valid except for polygon meshes
Arguments :
int : number of Y direction subdivisions : Not valid except for polygon meshes
Arguments :
int : number of Z direction subdivisions : Not valid except for polygon meshes
Arguments :
vec3 : coordinates of the first vertex composing the rectangle
Arguments :
vec3 : coordinates of the second vertex composing the rectangle
Arguments :
vec3 : coordinates of the third vertex composing the rectangle
Arguments :
vec3 : coordinates of the fourth vertex composing the rectangle
Arguments :
vec3 : XYZ components of the height
Arguments :
bool : top face
Arguments :
bool : bottom face
The local coordinate system becomes the reference.
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
#Create a polygon mesh from a cube with side of 200 (from the origin) and height of 500
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().create_primitive_box(None, 3, True, 1, 1, 1, [100, 0, -100], [100, 0, 100], [-100, 0, 100], [-100, 0, -100], [0, 500, 0], True, True)
xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_primitive_capsule
Creates a capsule.
Return value :
object
Arguments :
string : If "None", the default name is used
Arguments :
int : object type : 0 : generic, 1 : curved surface, 2 : unused, 3 : polygon mesh
Arguments :
bool : UV assigned : Not valid except for polygon meshes
Arguments :
int : number of U direction (circumference) subdivisions : Not valid except for polygon meshes
Arguments :
int : number of V direction (axial) subdivisions : Not valid except for polygon meshes
Arguments :
vec3 : the center coordinates of the lower hemisphere
Arguments :
float : the capsule radius
Arguments :
int : the crosswise plane 0 : Y Z, 1 : X Z, 2 : X Y
Arguments :
vec3 : XYZ components to the center of the upper hemisphere
The local coordinate system becomes the reference.
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
#Create a polygon mesh from a capsule at the origin with 16 UV subdivisions, radius of 400, and center-to-center length along the Y axis of 700
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().create_primitive_capsule(None, 3, True, 16, 16, [0, 0, 0], 400, 1, [0, 700, 0])
xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_primitive_cone
Creates a cone.
Return value :
object
Arguments :
string : If "None", the default name is used
Arguments :
int : object type : 0 : generic, 1 : curved surface, 2 : unused, 3 : polygon mesh
Arguments :
bool : UV assigned : Not valid except for polygon meshes
Arguments :
int : number of U direction (circumference) subdivisions : Not valid except for polygon meshes
Arguments :
int : number of V direction (height) subdivisions : Not valid except for polygon meshes
Arguments :
vec3 : the center coordinates of the bottom disk
Arguments :
float : the radius of the cone
Arguments :
int : the crosswise plane 0 : Y Z, 1 : X Z, 2 : X Y
Arguments :
vec3 : XYZ components of the height
Arguments :
bool : bottom face
The local coordinate system becomes the reference.
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
#Create a polygon mesh from a cone at the origin with 16 and 8 UV subdivisions, radius of 300, height of 500, and bottom face
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().create_primitive_cone(None, 3 , True, 16, 8, [0, 0, 0], 300, 1, [0,500, 0], True)
xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_primitive_cylinder
Creates a cylinder.
Return value :
object
Arguments :
string : If "None", the default name is used
Arguments :
int : object type : 0 : generic, 1 : curved surface, 2 : unused, 3 : polygon mesh
Arguments :
bool : UV assigned : Not valid except for polygon meshes
Arguments :
int : number of U direction (circumference) subdivisions : Not valid except for polygon meshes
Arguments :
int : number of V direction (height) subdivisions : Not valid except for polygon meshes
Arguments :
vec3 : the center coordinates of the bottom disk
Arguments :
float : the radius of the cylinder
Arguments :
int : the crosswise plane 0 : Y Z, 1 : X Z, 2 : X Y
Arguments :
vec3 : XYZ components of the height
Arguments :
bool : top face
Arguments :
bool : bottom face
The local coordinate system becomes the reference.
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
#Create a polygon mesh from a cylinder at the origin with 16 and 8 UV subdivisions, radius of 300, height of 500, and both top and bottom faces
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().create_primitive_cylinder(None, 3, True, 16, 8, [0,0,0],300, 1, [0, 500, 0], True, True)
xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_primitive_plane
Creates a rectangle.
Return value :
object
Arguments :
string : If "None", the default name is used
Arguments :
int : object type : 0 : generic, 1 : curved surface, 2 : unused, 3 : polygon mesh
Arguments :
bool : UV assigned : Not valid except for polygon meshes
Arguments :
int : number of U direction subdivisions : Not valid except for polygon meshes
Arguments :
int : number of V direction subdivisions : Not valid except for polygon meshes
Arguments :
vec3 : coordinates of the first vertex composing the rectangle
Arguments :
vec3 : coordinates of the second vertex composing the rectangle
Arguments :
vec3 : coordinates of the third vertex composing the rectangle
Arguments :
vec3 : coordinates of the fourth vertex composing the rectangle
The local coordinate system becomes the reference.
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
#Create a polygon mesh from a rectangle at the origin with 3 and 2 UV subdivisions and sides of 1000
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().create_primitive_plane(None, 3, True, 3, 2,[-500, 0, -500],[500, 0, -500],[500,0,500],[-500,0,500])
xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_primitive_pyramid
Creates a triangular pyramid.
Return value :
object
Arguments :
string : If "None", the default name is used
Arguments :
int : object type : 0 : generic, 1 : curved surface, 2 : unused, 3 : polygon mesh
Arguments :
bool : UV assigned : Not valid except for polygon meshes
Arguments :
int : number of Z direction subdivisions : Not valid except for polygon meshes
Arguments :
int : number of X direction subdivisions : Not valid except for polygon meshes
Arguments :
int : number of Y direction subdivisions : Not valid except for polygon meshes
Arguments :
vec3 : coordinates of the first vertex composing the rectangle
Arguments :
vec3 : coordinates of the second vertex composing the rectangle
Arguments :
vec3 : coordinates of the third vertex composing the rectangle
Arguments :
vec3 : coordinates of the fourth vertex composing the rectangle
Arguments :
bool : bottom face
The local coordinate system becomes the reference.
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
#Create a polygon mesh from a triangular pyramid at the origin with UV subdivisions of 1, 1, 1, sides of 1000, height of 600, and a bottom face
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().create_primitive_pyramid(None, 3, True, 1, 1, 1, [-500,0,-500],[500,0,-500],[500,0,500],[-500,0,500],[0,600,0],True)
xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_primitive_sphere
Creates a sphere.
Return value :
object
Arguments :
string : If "None", the default name is used
Arguments :
int : object type : 0 : generic, 1 : curved surface, 2 : unused, 3 : polygon mesh
Arguments :
bool : UV assigned : Not valid except for polygon meshes
Arguments :
int : number of U direction (circumference) subdivisions : Not valid except for polygon meshes
Arguments :
int : number of V direction (axial) subdivisions : Not valid except for polygon meshes
Arguments :
vec3 : coordinates of the center
Arguments :
float : the radius of the sphere
The local coordinate system becomes the reference.
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
#Create a polygon mesh from a sphere at the origin with 16 and 16 UV subdivisions and a radius of 300
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().create_primitive_sphere(None,3,True,16,16,[0,0,0],300)
xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_primitive_text
Create a 3D Text.
Return value :
Part Object
Arguments :
string : If "None", the default name is used
Arguments :
int : Primitive Type : 0 : Default Type (Uses 0)
Arguments :
bool : Output UV : True :Yes, False :No (Currently is unused)
Arguments :
vec3 : Position
Arguments :
int :Axis : 0 : YZ Plane, 1 : XZ Plane, 2 : XY Plane
Arguments :
int : Flip Layout : 0 : No Flip, 1 : Flip Horizontal, 2 : Flip Vertical, 3 : Flip Both Direction
Arguments :
vec3 : Height Vector
Arguments :
strings : Output Text String in UTF-8
Arguments :
strings : Font Name (OS X: Postscript font name; Windows: Font name)
Arguments :
int : Font Size
Arguments :
float : Character Spacing
Arguments :
int : Font Weight : Windows Only
Arguments :
bool : Italic Style : True : Yes, False : No (Windows Only)
begin_creating()、end_creating() are optional.
#Extrude 60, Character Spacing -1, Font Name 'Osaka'、Font Size 72, Output String 'Shade 3D'
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().create_primitive_text(None, 0, True, [0, 0, 0], 2, 0, [0, 0, -60], "Shade 3D", "Osaka", 72, -10, 0, False)
xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_primitive_torus
Creates a torus.
Return value :
object
Arguments :
string : If "None", the default name is used
Arguments :
int : object type : 0 : generic, 1 : curved surface, 2 : unused, 3 : polygon mesh
Arguments :
bool : UV assigned : Not valid except for polygon meshes
Arguments :
int : number of U direction (circumference) subdivisions : Not valid except for polygon meshes
Arguments :
int : number of V direction (axial) subdivisions : Not valid except for polygon meshes
Arguments :
vec3 : coordinates of the center
Arguments :
float : radius of the torus
Arguments :
float : radius of the disk that forms the torus
Arguments :
int : the crosswise plane 0 : Y Z, 1 : X Z, 2 : X Y
The local coordinate system becomes the reference.
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
#Create a polygon mesh from a torus at the origin with 16 and 16 UV subdivisions, a radius of 400, and a a disk radius of 100
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().create_primitive_torus(None, 3, True, 16, 16, [0, 0, 0], 400, 100, 1)
xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_rotator_joint
Creates a rotator joint.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
vec3 : position of one end point of the axis
Arguments :
vec3 : position of the other end point of the axis
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
The local coordinate system at the hierarchy where the object is created becomes the reference.
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
#Create a rotator joint along the X axis starting at the origin
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().create_rotator_joint([0.0, 0.0, 0.0],[100.0, 0.0, 0.0])
xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_scale_joint
Creates a scale joint.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
vec3 : the center point
Arguments :
vec3 : the target point
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
The local coordinate system at the hierarchy where the object is created becomes the reference.
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
#Create a scale joint of length 100 starting at the origin
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().create_scale_joint([0.0, 0.0, 0.0],[100.0, 0.0, 0.0])
xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_slider_joint
Creates a slider joint.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
vec3 : the starting point
Arguments :
vec3 : the ending point
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
The local coordinate system at the hierarchy where the object is created becomes the reference.
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
#Create a slider joint of length 100 starting from the origin
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().create_slider_joint([0.0, 0.0, 0.0],[100.0, 0.0, 0.0])
xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_sound_object
Creates a sound object.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
file_path
Arguments :
vec3 : the center point
Arguments :
float : radius
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
The local coordinate system at the hierarchy where the object is created becomes the reference.
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
#Create a sound object at the origin with radius 100, from sample.aiff
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().create_sound_object('sample.aiff',[0.0, 0.0, 0.0],100)
xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_sphere
Creates a sphere.
Return value :
sphere object
Arguments :
string : optional : If "None", the default name is used
Arguments :
vec3 : position
Arguments :
float : radius
The local coordinate system at the hierarchy where the object is created becomes the reference.
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
#Create a sphere at the origin with radius 100
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().create_sphere(None,[0.0, 0.0, 0.0],100)
xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_spotlight
Creates a spotlight.
Return value :
light object
Arguments :
string : optional : If "None", the default name is used
Arguments :
vec3 : position of the light
Arguments :
vec3 : the target position
Arguments :
float : the intensity
The local coordinate system at the hierarchy where the object is created becomes the reference.
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
#Create a spotlight along the X axis, starting at the origin, with intensity of 500
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().create_spotlight(None,[0.0, 0.0, 0.0],[100.0, 0.0, 0.0],500)
xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_surface_part
Creates a curved surface part.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
xshade.scene().begin_creating() xshade.scene().create_surface_part() xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_surface_replicator
Creates a surface replicator.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
xshade.scene().begin_creating() xshade.scene().create_surface_replicator() xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_switch_effector
Creates a switch.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
xshade.scene().begin_creating() xshade.scene().create_switch_effector() xshade.scene().end_creating()
create_uniscale_joint
Creates a uniscale joint.
Return value :
part object
Arguments :
vec3 : the center point
Arguments :
float : radius
Arguments :
string : optional : If omitted, the default name is used
The local coordinate system at the hierarchy where the object is created becomes the reference.
begin_creating() and end_creating() are optional.
#Create a uniscale joint with radius 100 at the origin
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().create_uniscale_joint([0.0, 0.0, 0.0],100)
xshade.scene().end_creating()
cut
Cuts the selected object to the clipboard.
xshade.scene().cut()
degenerate
Degenerates to a point.
xshade.scene().degenerate()
deselect_all_key_points
Deselects all motion points.
xshade.scene().deselect_all_key_points()
draw_figure_window
Draws the Figure Window.
xshade.scene().draw_figure_window()
end_ball_joint
Ends creation of a ball joint.
Use after begin_ball_joint() to stop creating the ball joint.
Always use as a set.
xshade.scene().end_ball_joint()
end_bone_joint
Ends creation of a bone joint.
Use after begin_bone_joint() to stop creating the bone joint.
Always use as a set.
xshade.scene().end_bone_joint()
end_creating
Ends creation of an object
Use after begin_creating() to stop creating the object.
Always use as a set.
#Create a uniscale joint with radius 100 at the origin
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().create_uniscale_joint([0.0, 0.0, 0.0],100)
xshade.scene().end_creating()
end_custom_joint
Ends creation of a custom joint.
Call after begin_custom_joint() to stop creating the custom joint.
Always use as a set.
#Create a custom joint
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_custom_joint()
xshade.scene().end_custom_joint()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
end_light_effector
Ends creation of a light joint.
Call after begin_light_effector() to stop creating the light joint.
Always use as a set.
#Create a light joint
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_light_effector()
xshade.scene().end_light_effector()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
end_line
Ends creation of a line object.
Call after begin_line() to stop creating the line object.
Always use as a set.
#Create an open line object composed of 2 points
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_line(None, False)
xshade.scene().append_point([0.0, 0.0, 0.0], None, None, None, None)
xshade.scene().append_point([0.0, 500.0, 0.0], None, None, None, None)
xshade.scene().end_line()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
end_morph_effector
Ends creation of a morph joint.
Call after begin_morph_effector() to stop creating the morph joint.
Always use as a set.
#Create a morph joint
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_morph_effector()
xshade.scene().end_morph_effector()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
end_part
Ends creation of a part.
Call after begin_part() to stop creating the part.
Always use as a set.
#Create a part
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_part()
xshade.scene().end_part()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
end_path_joint
Ends creation of a path joint.
Call after begin_path_joint() to stop creating the path joint.
Always use as a set.
#Create a path joint
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_path_joint()
xshade.scene().end_path_joint()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
end_path_replicator
Ends creation of a path replicator.
Call after begin_path_replicator() to stop creating the path replicator.
Always use as a set.
#Create a path replicator
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_path_replicator()
xshade.scene().end_path_replicator()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
end_polygon_mesh
Ends creation of a polygon mesh.
Call after #begin_polygon_mesh|begin_polygon_mesh() to stop creating the polygon mesh.
Always use as a set.
#Create a polygon mesh composed of 3 vertices and 3 edges
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_polygon_mesh(None)
xshade.scene().append_polygon_mesh_vertex([0.0,0.0,0.0])
xshade.scene().append_polygon_mesh_vertex([100.0,0.0,0.0])
xshade.scene().append_polygon_mesh_vertex([50.0,100.0,0.0])
xshade.scene().append_polygon_mesh_edge(0,1)
xshade.scene().append_polygon_mesh_edge(1,2)
xshade.scene().append_polygon_mesh_edge(2,0)
xshade.scene().end_polygon_mesh()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
end_rotator_joint
Ends creation of a rotator joint.
Call after begin_rotator_joint() to stop creating the rotator joint.
Always use as a set.
#Create a rotator joint with length 100 along the Y axis starting at the origin
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_rotator_joint((0.0,0.0,0.0),(0.0,100.0,0.0))
xshade.scene().end_rotator_joint()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
end_scale_joint
Ends creation of a scale joint.
Call after begin_scale_joint() to stop creating the scale joint.
Always use as a set.
#Create a scale joint of length 100 along the Y axis starting at the origin
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_scale_joint((0.0,0.0,0.0),(0.0,100.0,0.0))
xshade.scene().end_scale_joint()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
end_slider_joint
Ends creation of a slider joint.
Call after begin_slider_joint() to stop creating the slider joint.
Always use as a set.
#Create a slider joint of length 100 along the Y axis starting from the origin
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_slider_joint((0.0,0.0,0.0),(0.0,100.0,0.0))
xshade.scene().end_slider_joint()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
end_sound_object
Ends creation of a sound object.
Call after begin_sound_object() to stop creating the sound object.
Always use as a set.
#Create a sound object at the origin, with radius 100, from an aiff sound file
dialog = xshade.create_dialog_with_uuid()
file_path = dialog.ask_path(True, '*.aiff|aiff')
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_sound_object(file_path,(0.0,0.0,0.0),100)
xshade.scene().end_sound_object()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
end_surface_part
Ends creation of a curved surface part.
Call after begin_surface_part() to stop creating the curved surface part.
Always use as a set.
#Create a curved surface part
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_surface_part()
xshade.scene().end_surface_part()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
end_surface_replicator
Ends creation of a surface replicator.
Call after begin_surface_replicator() to stop creating the surface replicator part.
Always use as a set.
#Create a surface replicator
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_surface_replicator()
xshade.scene().end_surface_replicator()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
end_switch_effector
Ends creation of a switch.
Call after begin_switch_effector() to stop creating the switch.
Always use as a set.
#Create a switch
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_switch_effector()
xshade.scene().end_switch_effector()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
end_truetype
Ends creation of a TrueType (two-dimensional Bezier curve) object.
Call after begin_truetype() to stop creating the TrueType object.
Always use as a set.
#Create a TrueType object composed of 3 points
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_truetype(None, False)
xshade.scene().append_truetype_point(True,0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
xshade.scene().append_truetype_point(False,100.0, 100.0, 0.0)
xshade.scene().append_truetype_point(True,200.0, 0.0, 0.0)
xshade.scene().end_truetype()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
end_uniscale_joint
Ends creation of a uniscale joint.
Call after begin_uniscale_joint() to stop creating the uniscale joint.
Always use as a set.
#Create a uniscale joint with radius 100 at the origin
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
xshade.scene().begin_uniscale_joint((0.0,0.0,0.0),100)
xshade.scene().end_uniscale_joint()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
enter_create_line_mode
Enters Create Line Mode.
Arguments :
bool : True : closed line object, False : open line object
See also :
is_create_line_mode() Whether in Create Line Mode or not
exit_create_line_mode() Exits Create Line Mode
#Enter Create Line Mode for closed line objects
xshade.scene().enter_create_line_mode(True)
enter_modify_mode
Enters Modify Mode.
See also :
is_modify_mode() Whether in Modify Mode or not
exit_modify_mode() Exits Modify Mode
xshade.scene().enter_modify_mode()
exit_create_line_mode
Exits Create Line Mode.
See also :
enter_create_line_mode() Enters Create Line Mode
xshade.scene().exit_create_line_mode()
exit_modify_mode
Exits Modify Mode.
See also :
is_modify_mode() Whether in Modify Mode or not
enter_modify_mode() Enters Modify Mode
xshade.scene().exit_modify_mode()
export_scene
Exports the scene data
Arguments :
file_path
Arguments :
int :
| 0 | Preserves external references |
| 1 | Imports external references into the scene |
| 2 | Copies external references to the same folder |
#Export the scene data, preserving external references
dialog = xshade.create_dialog_with_uuid()
file_path = dialog.ask_path(False, '*.shd|shd')
xshade.scene().export_scene(file_path, 0)
export_with_uuid
Exports the file with uuid.
Arguments :
uuid: 128 bit value
Arguments :
file_path
See also :
uuid
#Export a file, specifying the uuid
dialog = xshade.create_dialog_with_uuid()
file_path = dialog.ask_path(False, '*.shd|shd')
xshade.scene().export_with_uuid('583DA72C-F329-469E-BEDE-A0349DEAC74B', file_path)
fit_to_window
Fits object to the Figure Window.
Type :
key : optional : If omitted, fits the whole scene, 0x01 : Fits the selected object
xshade.scene().fit_to_window()
flip_hide_faces
In Modify Mode, flips between hidden and nonhidden faces.
xshade.scene().flip_hide_faces()
force_update
Forces a screen redraw.
xshade.scene().force_update()
get_grid_shown
Returns the grid on/off value of the specified viewport.
Return value :
bool
Arguments :
int : view index
| 1 | top left viewport | 3 | top right viewport |
| 2 | bottom left viewport | 0 | bottom right viewport |
See also :
set_grid_shown
#Output the grid on/off value of the bottom right viewport
print xshade.scene().get_grid_shown(0)
get_ik
Gets the IK handling class.
Return value :
ik object
ik=xshade.scene().get_ik()
get_shape_by_name
Returns an object with the specified name.
Return value :
shape object
Arguments :
string : the object name
Arguments :
bool : False : only valid for names set by the user, True : also valid for default names
#Get "Closed Line", including default names, and make active (selected)
obj = xshade.scene().get_shape_by_name('Closed Line',True)
obj.activate()
get_shape_by_ordinal
Returns an object specified by ordinal number.
Return value :
shape object
Arguments :
int : ordinal number
Ordinals are determined by their order in the Brower, with the root part as 0.
See also :
shape.ordinal
#Make ordinal 1 active (selected)
xshade.scene().get_shape_by_ordinal(1).activate()
get_shape_by_position
Returns an object by position in the Browser.
Return value :
shape object
Arguments :
int tuple/list : list of positions
With the root part as the top of the hierarchy, classify the following in list format, and get the object using that hierarchical list.
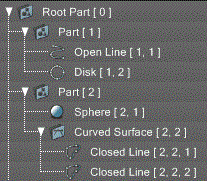
#Output the name of part [1] print xshade.scene().get_shape_by_position([1]).name #Output the name of the second closed line object in the curved surface print xshade.scene().get_shape_by_position([2,2,2]).name
get_shape_by_uuid
Returns an object specified by uuid.
Arguments :
uuid : 128 bit value
Return value :
shape object
See also :
uuid
#Select object with uuid eaf7a92f-160c-492b-9411-07a6efeeea92
xshade.scene().get_shape_by_uuid('eaf7a92f-160c-492b-9411-07a6efeeea92').activate()
get_shapes_by_name
Returns a tuple of objects with the specified name.
Return value :
shape object tuple
Arguments :
string : the object name
Arguments :
bool : False : only valid for names set by the user, True : also valid for default names
#Get "Disk", including default names, and make active (selected)
shapes = xshade.scene().get_shapes_by_name('Disk',True)
xshade.scene().active_shapes = shapes
get_view_rectangle
Returns the rectangular display area of the view specified by argument.
Return value :
rectangle
Arguments :
int : view index
| 1 | top left viewport | 3 | top right viewport |
| 2 | bottom left viewport | 0 | bottom right viewport |
| 4 | split view | ||
#Return the rectangular area of the bottom left viewport
print xshade.scene().get_view_rectangle(2)
hide_active
Hides the selected object.
xshade.scene().hide_active()
hide_inactive
Hides unselected objects.
xshade.scene().hide_inactive()
hide_select_faces
In Modify Mode, hides the selected faces of the selected object.
xshade.scene().hide_select_faces()
hide_unselect_faces
In Modify Mode, hides the unselected faces of the selected object.
xshade.scene().hide_unselect_faces()
iron
Applies Iron
xshade.scene().iron()
link
Links the selected part to the memorized object.
xshade.scene().link()
link_object
Creates a link object referencing the selected object.
Arguments :
vec3 : the center point
Arguments :
float3 : scale
Arguments :
float3 : rotation
Arguments :
float3 : translation
The local coordinate system at the hierarchy where the object is created becomes the reference.
#Create a link object at the origin
xshade.scene().link_object((0.0, 0.0, 0.0),None,None,None)
load_3DS
Imports a 3DS file.
Arguments :
file_path : extension (*.3ds) : If "None", opens a file dialog.
See also :
save_3DS
#Import a 3DS file
xshade.scene().load_3DS(None)
load_BVH
Imports a BVH file.
Arguments :
file_path : extension (*.bvh) : If "None", opens a file dialog.
#Import a BVH file
xshade.scene().load_BVH(None)
load_DXF
Imports a DXF file.
Arguments :
file_path : extension (*.dxf) : If "None", opens a file dialog.
See also :
save_DXF
#Import a DXF file
xshade.scene().load_DXF(None)
load_OBJ
Imports a wavefront OBJ file.
Arguments :
file_path : extension (*.obj) : If "None", opens a file dialog.
See also :
save_OBJ
#Import a wavefront OBJ file
xshade.scene().load_OBJ(None)
load_pose
Imports a Shade Pose file.
Arguments :
file_path : extension (*.shdpse) : If "None", opens a file dialog.
See also :
save_pose
#Import a Shade Pose file
xshade.scene().load_pose(None)
load_shape
Imports Shade object data.
Arguments :
file_path : extension (*.shd) : If "None", opens a file dialog.
Arguments :
bool : Optional (required if vec3 is specified)
True : Imports the scene using the origin of the imported scene as the reference point. Equivalent to the operation done while Option (Mac) or z (Win) is held.
False : Imports the scene using the cursor position of the imported scene as the reference point.
Arguments :
vec3 : coordinates of the import reference point : optional
See also :
save_shape
#Import shd object data, specifying the coordinates of the origin
xshade.scene().load_shape(None, True, [0.0, 0.0, 0.0])
load_template_image_to_front_view
Loads a template in the bottom left viewport.
Arguments :
file_path
#Load a jpg file in the bottom left viewport
dialog = xshade.create_dialog_with_uuid()
file_path = dialog.ask_path(True, '*.jpg|jpg')
xshade.scene().load_template_image_to_front_view(file_path)
load_template_image_to_pers_view
Loads a template in the top right viewport.
Arguments :
file_path
#Load a jpg file in the top right viewport
dialog = xshade.create_dialog_with_uuid()
file_path = dialog.ask_path(True, '*.jpg|jpg')
xshade.scene().load_template_image_to_pers_view(file_path)
load_template_image_to_side_view
Loads a template in the bottom right viewport.
Arguments :
file_path
#Load a jpg file in the bottom right viewport
dialog = xshade.create_dialog_with_uuid()
file_path = dialog.ask_path(True, '*.jpg|jpg')
xshade.scene().load_template_image_to_side_view(file_path)
load_template_image_to_top_view
Loads a template in the top left viewport.
Arguments :
file_path
#Load a jpg file in the top left viewport
dialog = xshade.create_dialog_with_uuid()
file_path = dialog.ask_path(True, '*.jpg|jpg')
xshade.scene().load_template_image_to_top_view(file_path)
load_text
Imports an XML text file.
Arguments :
file_path : extension (*.xmlshd) : If "None", opens a file dialog.
See also :
save_text
#Import an XML file
xshade.scene().load_text(None)
magnify
Magnifies the Figure Window.
Arguments :
vec3 : center position : optional : If omitted, the origin is used
#Magnify, centered on the origin
xshade.scene().magnify((0.0, 0.0, 0.0))
memorized_shape
Returns the memorized object.
Return value :
shape object : the memorized object
#Select the memorized object
xshade.scene().memorized_shape().activate()
memory
Memorizes the selected line object.
xshade.scene().memory()
move_object
Applies rotation, scaling, or translation to an object.
Arguments :
vec3 : the center point
Arguments :
float3 : scale
Arguments :
float3 : rotation
Arguments :
float3 : translation
See also :
copy_object
#Scale 1.5 in the X direction
xshade.scene().move_object([0.0, 0.0, 0.0], [1.5, 1.0, 1.0], None, None)
paste
Pastes an object into the scene from the clipboard.
xshade.scene().paste()
place_brother
Moves the selected object down.
Arguments :
int : the number to move
xshade.scene().place_brother(1)
place_child
Moves the selected object inside the below part.
Arguments :
int : the number of (child) parts in the hierarchy to move
xshade.scene().place_child(1)
place_parent
Moves the selected object to the top of the above hierarchy level.
Arguments :
int : the number of hierarchy levels to move
xshade.scene().place_parent(1)
place_sister
Moves the selected object forward.
Arguments :
int : the number to move
xshade.scene().place_sister(1)
print_
Prints the rendered image.
xshade.scene().print_()
read
Loads a scene from file.
Arguments :
file_path
Abandons the current scene and loads a scene (does not import it).
#Load a scene file
dialog = xshade.create_dialog_with_uuid()
file_path = dialog.ask_path(True, '*.shd|shd')
xshade.scene().read(file_path)
repeat
Applies Repeat.
Arguments :
int : repetitions : If omitted, 1
Only valid for move and copy operations.
xshade.scene().repeat()
reset_all_transformation
Resets the matrices of all parts within the selected part to unit matrices.
The object's morph state is not changed.
xshade.scene().reset_all_transformation()
reset_transformation
Resets the matrix of the selected part to a unit matrix.
The object's morph state is not changed.
xshade.scene().reset_transformation()
reverse
Applies Reverse.
xshade.scene().reverse()
revert_to_saved
Reverts the open Shade file to the saved state.
xshade.scene().revert_to_saved()
round_edge
Applies Round Edge.
Arguments :
float : radius
#Apply Round Edge with radius of 50
xshade.scene().round_edge(50)
save
Saves over the current scene.
If a new object, a file dialog is displayed.
See also :
xshade.open_scene()
xshade.scene().save()
save_3DS
Exports as a 3DS file.
Arguments :
file_path : extension (*.3ds) : If "None", opens a file dialog.
See also :
load_3DS
#Export a 3DS file
xshade.scene().save_3DS(None)
save_Animation_Master
Exports as an Animation:Master segment file.
Arguments :
file_path : extension (*.seg) : If "None", opens a file dialog.
#Export an Animation:Master segment file
xshade.scene().save_Animation_Master(None)
save_as
Displays a file dialog and saves the scene to file.
#Save the scene
xshade.scene().save_as()
save_DXF
Exports as a DXF file.
Arguments :
file_path : extension (*.dxf) : If "None", opens a file dialog.
See also :
load_DXF
#Export a DXF file
xshade.scene().save_DXF(None)
save_EPX
Exports as an EPix file.
Arguments :
file_path
It is necessary to specify both the Z Depth and object ID (or surface ID) passes with MultiPass and render ahead of time.
See also :
multipass_rendering Keep MultiPass on/off
set_image_layer_enable Layers on/off
#Export an epx file
dialog = xshade.create_dialog_with_uuid()
file_path = dialog.ask_path(False, '*.epx|epx')
xshade.scene().save_EPX(file_path)
save_FBX
Exports as an FBX file.
Arguments :
file_path : extension (*.fbx) : If "None", opens a file dialog.
#Export an FBX file
xshade.scene().save_FBX(None)
save_image
Saves the rendered image to file.
Arguments :
file_path
Specify the image format via the extension.
| Mac OSX | |
|---|---|
| PNG | *.png |
| TIFF | *.tif, *.tiff |
| Windows Bitmap | *.bmp |
| JPEG | *.jpg, *.jpeg |
| JPEG 2000 | *.jp2 |
| GIF | *.gif |
| OpenEXR | *.exr |
| Targa | *.tga |
| HDR | *.hdr |
| PFM | *.pfm |
| MPO | *.mpo |
| Flash | *.swf |
| Photoshop | *.psd |
| Windows | |
|---|---|
| BMP | *.bmp, *.dib, *.rle |
| JPEG | *.jpg, *.jpeg, *.jpe, *.jfif, *.jif |
| GIF | *.gif |
| TIFF | *.tif, *.tiff |
| PNG | *.png |
| OpenEXR | *.exr |
| Targa | *.tga |
| TARGA | *.targa |
| HDR | *.hdr |
| PFM | *.pfm |
| MPO | *.mpo |
| Flash | *.swf |
| Photoshop | *.psd |
#Save rendered image in psd format
dialog = xshade.create_dialog_with_uuid()
file_path = dialog.ask_path(False, '*.psd|psd')
xshade.scene().save_image(file_path)
save_images
Saves the rendered image to file in multi-layer format.
Arguments :
file_path
It is necessary to render in multi-layer format ahead of time.
#Save in Photoshop multi-layer format
dialog = xshade.create_dialog_with_uuid()
file_path = dialog.ask_path(False, '*.psd|psd')
xshade.scene().save_images(file_path)
save_local_axis
Saves the coordinate system (used temporarily).
Return value :
part
See also :
create_local_axis
xshade.scene().save_local_axis()
save_OBJ
Exports as a wavefront OBJ file.
Arguments :
file_path : extension (*.obj) : If "None", opens a file dialog.
See also :
load_OBJ
#Export a wavefront OBJ file
xshade.scene().save_OBJ(None)
save_pose
Exports a pose file.
Arguments :
file_path : extension (*.shdpse) : If "None", opens a file dialog.
See also :
load_pose
#Export a pose file
xshade.scene().save_pose(None)
save_RIB
Exports as a RIB file.
Arguments :
file_path : extension (*.rib) : If "None", opens a file dialog.
#Export an RIB file
xshade.scene().save_RIB(None)
save_shape
Exports as a Shade Shape file.
Arguments :
file_path : extension (*.shd) : If "None", opens a file dialog.
See also :
load_shape
#Export a Shade Shape file as sample.shd
xshade.scene().save_shape(None)
save_text
Exports as an XML text file.
Arguments :
file_path
See also :
load_text
#Export an XML text file
dialog = xshade.create_dialog_with_uuid()
file_path = dialog.ask_path(False, '*.xmlshd|xmlshd')
xshade.scene().save_text(file_path)
save_VRML
Exports as a VRML file.
Arguments :
file_path : extension (*.wrl) : If "None", opens a file dialog.
#Export a VRML file as sample.wrl
xshade.scene().save_VRML(None)
save_VRML_2
Displays a file dialog and exports as a VRML file.
xshade.scene().save_VRML_2()
scroll
Scrolls the Figure Window.
Arguments :
vec3 : center position
#Scroll to the origin
xshade.scene().scroll([0.0, 0.0, 0.0])
select_all
Selects the root object in Object Mode.
In Modify Mode, selects all the control points of the selected object.
xshade.scene().select_all()
select_brother
Selects the object after the selected object.
Return value :
bool
Arguments :
int : the number of objects after : optional : If omitted, 1
xshade.scene().select_brother()
select_child
Selects the objects in the part below the selected object.
Return value :
bool
Arguments :
xshade.scene().select_child()
select_parent
Selects the part above the selected object in the hierarchy.
Return value :
bool
Arguments :
int : the number of hierarchy levels above : optional : If omitted, 1
xshade.scene().select_parent()
select_sister
Selects the object before the selected object.
Return value :
bool
Arguments :
int : the number of objects before : optional : If omitted, 1
xshade.scene().select_sister()
sequence_world_to_device_matrix
Returns a matrix that converts the world coordinate system of the specified sequence to device coordinates.
Arguments :
int
Return value :
mat4
print xshade.scene(). sequence_world_to_device_matrix(0)
sequence_world_to_perspective_matrix
Returns a matrix that converts the world coordinate system of the specified sequence to perspective coordinates.
Arguments :
int
Return value :
mat4
print xshade.scene(). sequence_world_to_perspective_matrix(0)
sequence_world_to_view_matrix
Returns a matrix that converts the world coordinate system of the specified sequence to view coordinates.
Arguments :
int
Return value :
mat4
print xshade.scene(). sequence_world_to_view_matrix(0)
set_grid_shown
Sets the grid on/off value of the specified viewport.
Arguments :
int : view index
| 1 | top left viewport | 3 | top right viewport |
| 2 | bottom left viewport | 0 | bottom right viewport |
Arguments :
bool
See also :
get_grid_shown
#Set grid to 'on' in the bottom right viewport
xshade.scene().set_grid_shown(0, True)
show_active
Displays the selected object.
xshade.scene().show_active()
show_all
Displays all objects
xshade.scene().show_all()
show_all_faces
In Modify Mode, displays all the faces of the selected object.
xshade.scene().show_all_faces()
shrink
Shrinks the Figure Window.
Arguments :
vec3 : center position : optional
xshade.scene().shrink()
smooth
Applies Smooth.
xshade.scene().smooth()
solid_clear
Returns the original state of an extruded or revolved solid.
xshade.scene().solid_clear()
solid_extrude
Creates an extruded solid.
Arguments :
float3 : vector of the extruded distance
#Create an extruded solid of length 500 in the Z direction
xshade.scene().solid_extrude((0.0, 0.0, 500.0))
solid_revolve
Creates a revolved solid.
Arguments :
vec3 : one end point of the axis of revolution
Arguments :
vec3 : the other end point of the axis of revolution
#Create a revolved solid along the Y axis from the origin to 10
xshade.scene().solid_revolve((0.0, 0.0, 0.0), (0.0, 10.0, 0.0))
sweep
Applies Sweep.
xshade.scene().sweep()
switch
Applies Switch.
xshade.scene().switch()
unsmooth
Applies Unsmooth.
xshade.scene().unsmooth()
update_figure_window
Redraws the Figure Window.
xshade.scene().update_figure_window()
use_global
Uses global coordinates for the Figure Window display.
xshade.scene().use_global()
use_local
Uses the local coordinates of the selected object for the Figure Window display.
xshade.scene().use_local()
use_local_axis
Uses the specified coordinate system.
Arguments :
string
xshade.scene().use_local_axis('coordinate system[1]')
write
Saves a Shade scene file.
Arguments :
file_path : extension (*.shd) : If "None", opens a file dialog.
#Save a Shade scene file
xshade.scene().write(None)
write_compatible
Saves a Shade scene file after adding compatibility information.
Arguments :
file_path
#Save after adding compatibility information
dialog = xshade.create_dialog_with_uuid()
file_path = dialog.ask_path(False, '*.shd|shd')
xshade.scene().write_compatible(file_path)
write_noncompatible
Saves a Shade scene file without adding compatibility information.
Arguments :
file_path
#Save without adding compatibility information
dialog = xshade.create_dialog_with_uuid()
file_path = dialog.ask_path(False, '*.shd|shd')
xshade.scene().write_noncompatible(file_path)
write_R4compatible
Saves a Shade scene file after adding R4 compatibility information.
Arguments :
file_path
#Save after adding R4 compatibility information
dialog = xshade.create_dialog_with_uuid()
file_path = dialog.ask_path(False, '*.shd|shd')
xshade.scene().write_R4compatible(file_path)
write_xml
Saves a Shade scene file as XML.
Arguments :
file_path
dialog = xshade.create_dialog_with_uuid() file_path = dialog.ask_path(False, '*.shd|shd') xshade.scene().write_xml(file_path)
Property Details
active_shapes
The list of currently selected objects.
- Get
- Set
Type :
shape object
#Output names of selected objects in order
for i in xshade.scene().active_shapes:
print i.name
animation_settings
#Output the frame rate
print xshade.scene().animation_settings.frame_rate
background
#Output the color of the bottom hemisphere
print xshade.scene(). background.lower_base_color
camera
#Output the position of the eye point
print xshade.scene().camera.eye
can_create
Whether or not there is a functional restriction on creating new objects.
- Get
- Set
Type :
bool : True is the normal value.
print xshade.scene().can_create
can_export_foreign
Whether or not there is a functional restriction on exporting to formats unrelated to Shade.
- Get
- Set
Type :
bool : True is the normal value.
print xshade.scene().can_export_foreign
can_export_native
Whether or not there is a functional restriction on exporting to Shade-related formats.
- Get
- Set
Type :
bool : True is the normal value.
print xshade.scene().can_export_native
can_save
Whether or not there is a functional restriction on saving the scene.
- Get
- Set
Type :
bool : True is the normal value.
print xshade.scene().can_save
can_save_rendered_image
Whether or not there is a functional restriction on saving the rendered image to file.
- Get
- Set
Type :
bool : True is the normal value.
print xshade.scene().can_save_rendered_image
center
The coordinates of the center of each of the viewports, other than the perspective view.
- Get
- Set
Type :
vec3
print xshade.scene().center
color_mode
Color mode of the Figure Window display.
- Get
- Set
Type :
bool
print xshade.scene().color_mode
correction
#Output the contrast
print xshade.scene().correction.contrast
current_camera
The index value of the currently selected camera.
- Get
- Set
Type :
int
print xshade.scene().current_camera
current_cursor_position
Current coordinates value of the 3D cursor in the Figure Window.
- Get
- Set
Type :
vec3
print xshade.scene().current_cursor_position
cursor_plane
The cursor plane in the perspective view.
- Get
- Set
Type :
int : 0 : YZ, 1 : XZ, 2 : XY, 3 : screen
print xshade.scene().cursor_plane
cursor_position
Coordinates value of the 3D cursor in the Figure Window (the clicked position).
- Get
- Set
Type :
vec3
print xshade.scene().cursor_position
default_bevel_radius
Default value of Round Edge and Bevel Edge.
- Get
- Set
Type :
float
print xshade.scene().default_bevel_radius
default_disk_radius
Default radius of a disk.
- Get
- Set
Type :
float
print xshade.scene().default_disk_radius
default_light_radius
Default light intensity.
- Get
- Set
Type :
float
print xshade.scene().default_light_radius
default_radius
Default radius of Round Edge and Bevel Edge for line objects.
- Get
- Set
Type :
float
print xshade.scene().default_radius
default_sphere_radius
Default radius of a sphere.
- Get
- Set
Type :
float
print xshade.scene().default_sphere_radius
dirty
Whether or not the scene is dirty.
- Get
- Set
Type :
bool
The scene is dirty if any operation is done in an open scene.
When closing dirty scenes a dialog is displayed asking, "Do you want to save the changes ...?"
print xshade.scene().dirty
display
#Display the grid in all viewports
xshade.scene().display.grid = True
distant_light
#Output the number of the selected Distant Light
print xshade.scene().distant_light.active_item
figure_view_mode
Figure Window view mode.
- Get
- Set
Type :
int : view index
| 1 | top left viewport | 3 | top right viewport |
| 2 | bottom left viewport | 0 | bottom right viewport |
| 4 | split view | ||
print xshade.scene().figure_view_mode
figure_window
#Hide the Figure Window
xshade.scene().figure_window.hide()
file_path
File path of the saved scene.
- Get
- Set
Type :
file_path
print xshade.scene().file_path
fog
#Output the fog color
print xshade.scene().fog.color
fps
Scene fps.
- Get
- Set
Type :
int
print xshade.scene().fps
grid
Grid display on/off.
- Get
- Set
Type :
bool
print xshade.scene().grid
insertion_shape
Shape class of the object at the inserted position when creating an object with begin_creating().
- Get
- Set
Type :
shape object
#Output the name of the object at the inserted position when creating a part
xshade.scene().begin_creating()
obj = xshade.scene().insertion_shape
xshade.scene().begin_part()
xshade.scene().end_part()
xshade.scene().end_creating()
print obj.name
is_create_line_mode
Whether or not in Create Line Mode.
- Get
- Set
Type :
bool
print xshade.scene().is_create_line_mode
is_locked
Whether or not the file is locked.
- Get
- Set
Type :
bool
print xshade.scene().is_locked
is_modify_mode
Whether or not in Modify Mode.
- Get
- Set
Type :
bool
print xshade.scene().is_modify_mode
is_motion_playing
Whether or not the Motion Window is playing
- Get
- Set
Type :
bool
print xshade.scene().is_motion_playing
keyframes
#Delete the selected keyframe
xshade.scene().keyframes.delete_active_keyframes()
large_cursor
Large Cursor display on/off.
- Get
- Set
Type :
bool
print xshade.scene().large_cursor
large_point
Large Point display on/off
- Get
- Set
Type :
bool
print xshade.scene().large_point
lathe_rotation
Lathe rotation.
- Get
- Set
Type :
quaternion
print xshade.scene().lathe_rotation
light_scale
Light scale.
- Get
- Set
Type :
float
print xshade.scene().light_scale
local
Reference part of the local coordinates.
- Get
- Set
Type :
shape object
Getting is possible in local mode
#Output the name of the reference part
print xshade.scene().local.name
local_matrix
Local coordinates mode transformation matrix.
- Get
- Set
Type :
mat4
print xshade.scene().local_matrix
manip_type
The manipulator type.
- Get
- Set
Type :
int : 0: none, 1: Universal, 2: Translate, 3: Scale, 4: Rotate
print xshade.scene().manip_type
mapping_modify_mode
Whether or not in Mapping Modify Mode.
- Get
- Set
Type :
bool
print xshade.scene().mapping_modify_mode
native_to_user_unit
Coefficient which converts native units (mm) to user-defined units.
- Get
- Set
Type :
float
See also :
user_to_native_unit
print xshade.scene().native_to_user_unit
number_of_appended_points
The number of control points of the line object being created.
- Get
- Set
Type :
int
#Output the number of control points while creating a line object #Output 0, 1, 2 in order from the top xshade.scene().begin_creating() xshade.scene().begin_line(None, False) print xshade.scene().number_of_appended_points xshade.scene().append_point([0.0, 0.0, 0.0], None, None, None, None) print xshade.scene().number_of_appended_points xshade.scene().append_point([0.0, 500.0, 0.0], None, None, None, None) print xshade.scene().number_of_appended_points xshade.scene().end_line() xshade.scene().end_creating()
number_of_cameras
The number of cameras.
- Get
- Set
Type :
int
print xshade.scene().number_of_cameras
number_of_memorized_shapes
The number of memorized objects.
- Get
- Set
Type :
int
Returns 1 if there are memorized objects, 0 if there are none.
print xshade.scene().number_of_memorized_shapes
number_of_metacameras
The number of meta-cameras.
- Get
- Set
Type :
int
print xshade.scene().number_of_metacameras
pers_grid
Perspective Grid display on/off.
- Get
- Set
Type :
bool
print xshade.scene().pers_grid
pivot_position
The pivot coordinates.
- Get
- Set
Type :
vec3
print xshade.scene().pivot_position
pixel_size
The state of magnification of the Figure Window.
- Get
- Set
Type :
int : 1 dot is 10
Returns the size in the scene of 1 pixel of the display.
The width of one square of the Minor Grid will be 10 times this.
print xshade.scene().pixel_size
radiosity
#Output the minimum mesh spacing
print xshade.scene().radiosity.solution_minimum_mesh_spacing
rendering
#Render
xshade.scene().rendering.render()
selection_method
The Toolbox Selection Mode.
- Get
- Set
Type :
int :
| 0 | Box |
| 1 | Lasso |
| 2 | Trace |
Reflect changes using tool_box_view().update()
#Change Selection Mode to Lasso
xshade.scene().selection_method = 1
xshade.tool_box_view().update()
selection_mode
The Mesh Selection Mode.
- Get
- Set
Type :
int :
| 0 | Face selection |
| 1 | Edge selection |
| 2 | Vertex selection |
#Change Mesh Selection Mode to Vertex
xshade.scene().selection_mode = 2
sequence_mode
Whether the scene is in Sequence Mode or not.
- Get
- Set
Type :
bool
print xshade.scene().sequence_mode
sequence_value
The sequence value of the Motion Window.
- Get
- Set
Type :
float
print xshade.scene().sequence_value
shape
#Output the uuid of the Root Part
print xshade.scene().shape.uuid
show_normals
Whether to show normals or not
- Get
- Set
Type :
bool
print xshade.scene().show_normals
snap
Snap on/off.
- Get
- Set
Type :
bool
print xshade.scene().snap
step_frames
The number of step frames of the animation (float).
- Get
- Set
Type :
float
print xshade.scene().step_frames
template
Template display on/off.
- Get
- Set
Type :
bool
print xshade.scene().template
unit
The unit value.
- Get
- Set
Type :
int :
| 0 | mm (Shade's native units) |
| 1 | cm |
| 2 | m |
| 3 | km |
| 4 | inches |
| 5 | feet |
| 6 | yards |
| 7 | miles |
print xshade.scene().unit
user_to_native_unit
Coefficient which converts user-defined units to native units (mm).
- Get
- Set
Type :
float
See also :
native_to_user_unit
print xshade.scene().user_to_native_unit
user_to_world_matrix
Matrix that converts the user coordinate system to world coordinates.
- Get
- Set
Type :
mat4
The user coordinate system is the coordinate system of the Figure Window display, taking into account rotation and Local or Global Mode.
It is used such as when taking into account the movement or rotation of an object.
See also :
world_to_user_matrix
print xshade.scene().user_to_world_matrix
window_frame
The Figure Window frame.
Type :
rectangle
print xshade.scene().window_frame
work_plane
Work plane on/off.
- Get
- Set
Type :
bool
print xshade.scene().work_plane
world_to_device_matrix
Matrix that converts the world coordinate system to device coordinates.
- Get
- Set
Type :
mat4
A matrix which rotates, translates, and normalizes the world coordinates based on the camera position, direction, and bank.
Moves the eye point to the origin and aligns the line of sight with the Z axis.
The device coordinate system normalizes the X and Y coordinates to match the X and Y positions of the rendered image (representing the field of view), as measured in pixels from the top left of the rendered image.
print xshade.scene().world_to_device_matrix
world_to_perspective_matrix
Matrix that converts the world coordinate system to the perspective coordinate system of the active camera.
- Get
- Set
Type :
mat4
A matrix which rotates, translates, and normalizes the world coordinates based on the camera position, direction, and bank.
Moves the eye point to the origin and aligns the line of sight with the Z axis.
Normalizes the coordinates in the field of view to fit within -1.0 and 1.0 vertically and horizontally, and within 0.0 and 1.0 in depth. Because coordinates outside this range are outside the field of view, clipping will be performed on those coordinates.
print xshade.scene().world_to_perspective_matrix
world_to_user_matrix
Matrix that converts the world coordinate system to user coordinates.
- Get
- Set
Type :
mat4
The user coordinate system is the coordinate system of the Figure Window display, taking into account the units, rotation of the object and Local or Global Mode.
It is used such as when taking into account the movement or rotation of an object.
See also :
user_to_world_matrix
print xshade.scene().world_to_user_matrix
world_to_view_matrix
Matrix that converts the world coordinate system to the view coordinate system of the active camera.
- Get
- Set
Type :
mat4
Applies a matrix with eye point at the origin which rotates and translates the world coordinates based on the camera position, direction, and bank, and aligns the line of sight with the Z axis.
Perspective transformation is not done.
print xshade.scene().world_to_view_matrix