Camera Window
Select View > Camera or click the Camera tab of the Aggregate Window to open the Camera Window.
Use the Camera Window to adjust the camera settings and change the Perspective View's field of view.
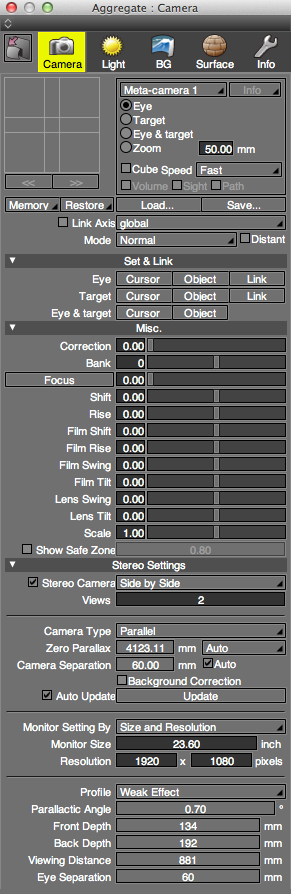
Basic Settings
- Virtual Joystick
- Dragging the virtual joystick from the center will move either the Eye, Target, Eye & Target, or Zoom, based on the selected radio button, changing the field of view.
Select Eye to move the viewpoint in the dragged direction. Select Target to move the target point in the dragged direction.
Select Eye & Target to move both the viewpoint and target point in parallel in the dragged direction.Note When Eye & Target is selected, hold the Ctrl key (Windows) or Option key (Mac OS) while moving the virtual joystick up or down to move the viewpoint and target point forwards or backwards in parallel.
Select Zoom and drag left or right to change the focal length (angle of view). Drag up or down to zoom in or out.Note When Zoom is selected, hold the Ctrl key (Windows) or Option key (Mac OS) while moving the virtual joystick up or down to move the target point along the line of sight while keeping the viewpoint locked. The display of the Perspective View does not change.
- << (Back) Button
- To step backward through changes to the camera, click the Back button.
- >>(Forward) Button
- To step forward through changes to the camera, click the Forward button.
- Select Camera Pop-up Menu
- This menu is used to select the active camera used for the Perspective View and rendering. When a camera object is created, it is added to the Select Camera pop-up menu. Select Remove to delete the currently selected camera.
- Info Button
- When a plugin with camera custom attributes is installed, click this button to display the custom attributes.
- Eye
- Changes the operation of the virtual joystick to Eye.
- Target
- Changes the operation of the virtual joystick to Target.
- Eye & Target
- Changes the operation of the virtual joystick to Eye & Target.
- Zoom
- Changes the operation of the virtual joystick to Zoom.
- Focal Length
- Displays the focal length of the camera. When zooming in or out the values will change in real time. Click in the textbox to enter a new value for the focal length.
- Cube Checkbox
- Selecting this checkbox will display a straight line connecting an eye and a target, a cube indicating the range of main objects, and X axis, Z axis and horizontal line of a global coordinate in the Perspective View during volume change.
- Speed
- Adjusts the rate at which the camera changes relative to distance dragged using the virtual joystick.
- Memory Pop-up Menu
- This menu is used to create an object from the current camera's Eye and Target points.
- Restore Pop-up Menu
- This menu is used to create a camera from the currently selected object.
- Load...
- Loads a camera settings file (.shdcmr, .xmlshdcmr).
- Save...
- Saves the current Camera Window settings as a camera settings file (.shdcmr, .xmlshdcmr).
- Link Axis
- Synchronizes camera switching with the settings of the saved permanent coordinate axis. Select the Link Axis checkbox and select the coordinate system to be linked from the pop-up menu. Making this setting in advance and selecting the camera linked to the coordinate system from the View pop-up menu enables you to switch the view in sync with the coordinate system.
- Mode
- This menu is used to set limits on the line of sight.
- Distant
- Places a distant screen at the target position and uses parallel projection. In this case, the color of the background would result from multiplicative synthesis between the background color of either the upper hemisphere or lower hemisphere, whichever is closer to the center of the Perspective View and the mapping slider value of the mapping color. Background patterns are hidden.
Set & Link Settings
Use these buttons to control the positions of the Eye and Target.
Fit
- Fit to Selection
- Fits the selection in the field of view.
Eye
- Cursor
- Moves the eye to the position of the 3D cursor.
- Object
- Moves the eye to the center of the selection. Clicking the Object button in Modify Mode will set the eye to the center of the selected control points.
- Link
- Moves the eye to the center of the selection and links the camera so that it follows object movement. To cancel the camera eye link, click this button again (the label changes to Unlink).
Target
- Cursor
- Moves the target to the position of the 3D cursor.
- Object
- Moves the target to the center of the selection. Clicking the Object button in Modify Mode will set the eye to the center of the selected control points.
- Link
- Moves the target to the center of the selection and links the camera so that it follows object movement. To cancel the camera eye link, click this button again (the label changes to Unlink).
Eye & Target
- Cursor
- Moves the eye and target so that the 3D cursor position serves as the target with the relative positions of the current eye and target maintained.
- Object
- Moves the eye and target so that the center of the object serves as the target with the relative positions of the current eye and target maintained. Clicking the Object button in Modify Mode will set the eye in the center of the selected control points.
Display Settings
- Rendering Area
- Displays the rendering area in Perspective View.
- Camera Object Settings
- Checkboxes in this group are active when a camera object is selected from the Camera Selection pop-up menu. You can change the selected camera object in the Figure Window.
- Scale
- Scales the field of view in Perspective View. The camera can be zoomed without changing the angle or viewpoint.
- Show Safe Zone
- Displays the safe zone for video output for the Perspective View, camera or meta-camera. You can scale the relative size of the display area by entering a percentage in the textbox.
Misc. Settings
- Correction
- Corrects vertical perspective distortion. When the value is 1, the vertical perspective distortion is completely corrected. Conversely, when the value is 2 or above, the vertical perspective distortion is emphasized.
- Bank
- Rotates the field of view. Negative values rotate the volume counterclockwise. Positive values rotate the volume clockwise.
- Focus Button
- Sets the surface vertical to the sight for the 3D cursor position as the object surface.
- Focus Slider & Textbox
- Simulates the effects of depth of field when path tracing is performed. If a value other than 0 is set, the depth of field is processed with reference to the object surface set by the Focus button. The larger the value, the shallower the depth of field and the larger the degree of the focus value.
- Shift
- Performs tilt correction. Shifts the line of sight horizontally by shifting the Eye point. As a result of this shifting, surfaces vertical to the line of sight seem to shift horizontally according to the distance from the line of sight.
- Rise
- Performs tilt correction. Shifts the line of sight vertically by shifting the Eye point. As a result of this shifting, surfaces vertical to the line of sight seem to shift vertically according to the distance from the line of sight.
- Film Shift
- Performs tilt correction. Shifts the line of sight horizontally by shifting the Target point. As a result of this shifting, surfaces vertical to the line of sight seem to shift horizontally according to the distance from the line of sight.
- Film Rise
- Performs tilt correction. Shifts the line of sight vertically by shifting the Target point. As a result of this shifting, surfaces vertical to the line of sight seem to shift vertically according to the distance from the line of sight.
- Film Swing
- Performs optical axis correction. Change the left and right perspectives by tilting the line of sight left or right and by tilting the surface vertical to the optical axis and the film.
- Film Tilt
- Performs optical axis correction. Change the up and down perspectives by tilting the line of sight upward or downward and by tilting the surface vertical to the optical axis and the film.
- Lens Swing
- Performs optical axis correction. Change the left and right foci by tilting the optical axis left or right and by tilting the focal plane and the film. This effect is only enabled when rendering with Path Tracing.
- Lens Tilt
- Performs optical axis correction. Change the up and down foci by tilting the optical axis up or down and by tilting the focal plane and the film. This effect is only enabled when rendering with Path Tracing.
Stereo Settings
These settings affect the stereo image when a stereo camera is used.
- Stereo Camera Checkbox
- Select the Stereo Camera checkbox when rendering a stereo image.
- Stereo Camera Pop-up Menu
- Specifies the stereoscopic rendering method.
- Views
- Specifies the number of viewpoints.
- Camera Type
- Specifies the camera arrangement.
- Zero Parallax Textbox
- To enter a value for zero parallax, select User Defined from the Zero Parallax pop-up menu.
- Specifies the distance (in the scene) at which the parallax between the left and right cameras is zero. Objects in front of this point appear to jump out of the screen (negative parallax), whereas objects behind this point appear to be behind the screen (positive parallax).
- Zero Parallax Pop-up Menu
- Specifies the method used to set the zero parallax distance.
- Camera Separation
- Specifies the distance (in the scene) to move the camera left and right.
- Auto
- When selected, the camera separation is calculated automatically.
- Background Correction
- When selected, the zero parallax and camera separation distance is adjusted for the background.
If an image has been mapped to the background, selecting Background Correction results in a weaker 3D effect but prevents extreme disparity between the background and objects that appear before it.
If the background is not mapped, deselect this option to maximize the 3D effect. - Auto Update
- Stereo settings are automatically updated after any camera operations.
- Update
- Calculates the virtual screen and camera separation distance based on the objects in the scene.
- Monitor Setting By
- Provides a series of device based profiles for optimizing stereoscopic output based on size and resolution.
- Monitor Size
- The screen size (diagonally).
- Resolution
- The maximum screen resolution.
- Profile
- This menu is used to adjust the stereoscopic effects. In addition to presets that automatically adjust the settings based on the monitor settings, you can enter values for custom adjustments.
- Parallactic Angle
- Available when Custom (Parallactic Angle) is selected for the Profile.
Specifies the angle used to create a sense of depth. Larger values result in a greater perception of depth. To avoid eye strain and fatigue when viewing for extended periods of time, values less than 1.0 are recommended. - Front Depth
- Available when Custom (Depth Off Screen) is selected for the Profile.
Specifies the virtual distance in front of the screen that objects appear. - Back Depth Textbox
- Available when Custom (Depth Off Screen) is selected for the Profile.
Specifies the virtual distance behind the screen that objects appear. - Viewing Distance Textbox
- Available when Custom (Parallactic Angle) or Custom (Depth Off Screen) is selected for the Profile.
Specifies the distance from the screen to the viewing point. - Eye Separation Textbox
- Available when Custom (Parallactic Angle) or Custom (Depth Off Screen) is selected for the Profile.
Specifies the interaxial (the distance between left and right eyes). 50mm is generally appropriate for children.